HP PageWide XL 8000 User guide - Page 109
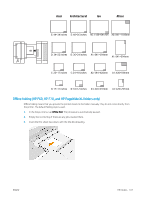
Folding styles, DIN B 210 × 297 mm back panel covered
 |
View all HP PageWide XL 8000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 109 highlights
Folding styles The folder can fold pages in two different ways: ● Fan fold, in which folds are perpendicular to the printing direction ● Cross fold, in which folds are parallel to the printing direction Folding styles are usually based on DIN B or DIN C style: DIN B The top and bottom folds are always on opposite sides. If this is what you want, select a folding style below marked with an asterisk, as these are the ones based on DIN B style. All folding styles that include a filing option (tab or filing margin) need to follow that configuration. It requires compensation folds in many formats since the last page's end needs to be in a certain position for the filing option (hanging strip/filing margin). As those packets have more, unevenly distributed, folds, they tend to be thicker on one side making them topple over when you pile them up. Furthermore, the stack gets bigger. DIN C The top and bottom folds are not necessarily on opposite sides. There are no compensation folds, which means that you are getting a thinner and more even stack when plotting a lot of prints and keeping them in one stack, either in plastic jackets or in envelopes/ folders. DIN ● DIN A 190+20 × 297 mm (with binding edge)* 190 mm width, 20 mm margin, 297 mm height ● DIN B 210 × 297 mm (back panel covered)* 210 mm width, 297 mm height ENWW HP folders 103