HP ProLiant DL360e HP Smart Update Firmware DVD User Guide - Page 33
Enabling ports in HP SUM, For Windows Operating Systems, For Linux
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL360e manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 33 highlights
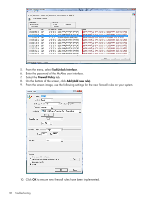
Enabling ports in HP SUM The ports that HP SUM uses cannot be configured by the end user. When HP SUM port initiates communications to remote targets, it uses several well-known ports depending on the operating system. For Windows, it uses ports 138 and 445 to connect to remote targets (equivalent to remote and file print share functionality). For Linux, HP SUM uses port 22 (SSH) to start the communications with the remote target. HP SUM uses defined ports to communicate between the remote target and the workstation where HP SUM is executing. When you run HP SUM, it uses the administrator/root privileges to dynamically register the port with the default Windows and Linux firewalls for the length of the application execution, closes and deregisters the port. All communications are over a SOAP server using SSL with additional functionality to prevent man-in-the-middle, packet spoofing, packet replay, and other attacks. The randomness of the port helps prevent port scanning software from denying service to the application. The SOAP server is deployed on the remote target using the initial ports 138, 445, and 22, and then allocates another independent port for communications back to the workstation where HP SUM is running. During shutdown of HP SUM, the SOAP server shuts down and is removed from the target server, leaving the log files. To deploy software to remote targets on the secure networks using HP SUM, the following ports are used. For Windows Operating Systems Ports Description Ports 445 and 137/138/139 (Port 137 is used only if you are using NetBIOS naming service.) These ports are needed to connect to the remote ADMIN$ share on target servers. These are the standard ports Windows servers use to connect to remote file shares. If you can connect remotely to a remote Windows file share on the target server, then you have the right ports open. Port 62286 Ports 80 and 63000 This port is the default for some internal communications. It is the listing on the remote side if there is no conflict. If a conflict occurs, the next available one is used. The logs are passed to the target and the logs are retrieved via an internal secure web server that uses port 80 if it is available or port 63000 if it is not. This support enables updates of the iLO firmware without the need to access the host server and allows servers running VMware or other virtualization platforms to update iLO without the need to reboot their server or migrate their virtual machines to other servers. For Linux Port Port 22 Port 62286 Ports 80 and 63000 Description This port is establishes a connection to the remote Linux server via SSH. This port is the default for some internal communications. It is used for listening on the remote side if there is no conflict. If a conflict occurs, the next available one is used. The logs are passed to the target and the logs are retrieved via an internal secure web server that uses port 80 if it is available or port 63000 if it is not. This support allows updates of the iLO firmware without the need to access the host server and allows servers running VMware or other virtualization platforms to update their iLO without the need to reboot their server or migrate their virtual machines to other servers. Recovering from a blocked program on Microsoft Windows 33