HP ProLiant SL2500 HP ROM-Based Setup Utility User Guide - Page 184
NMI Debug Button, Virtual Install Disk, Secondary IDE Channel Support, BIOS Enhanced RAID
 |
View all HP ProLiant SL2500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 184 highlights
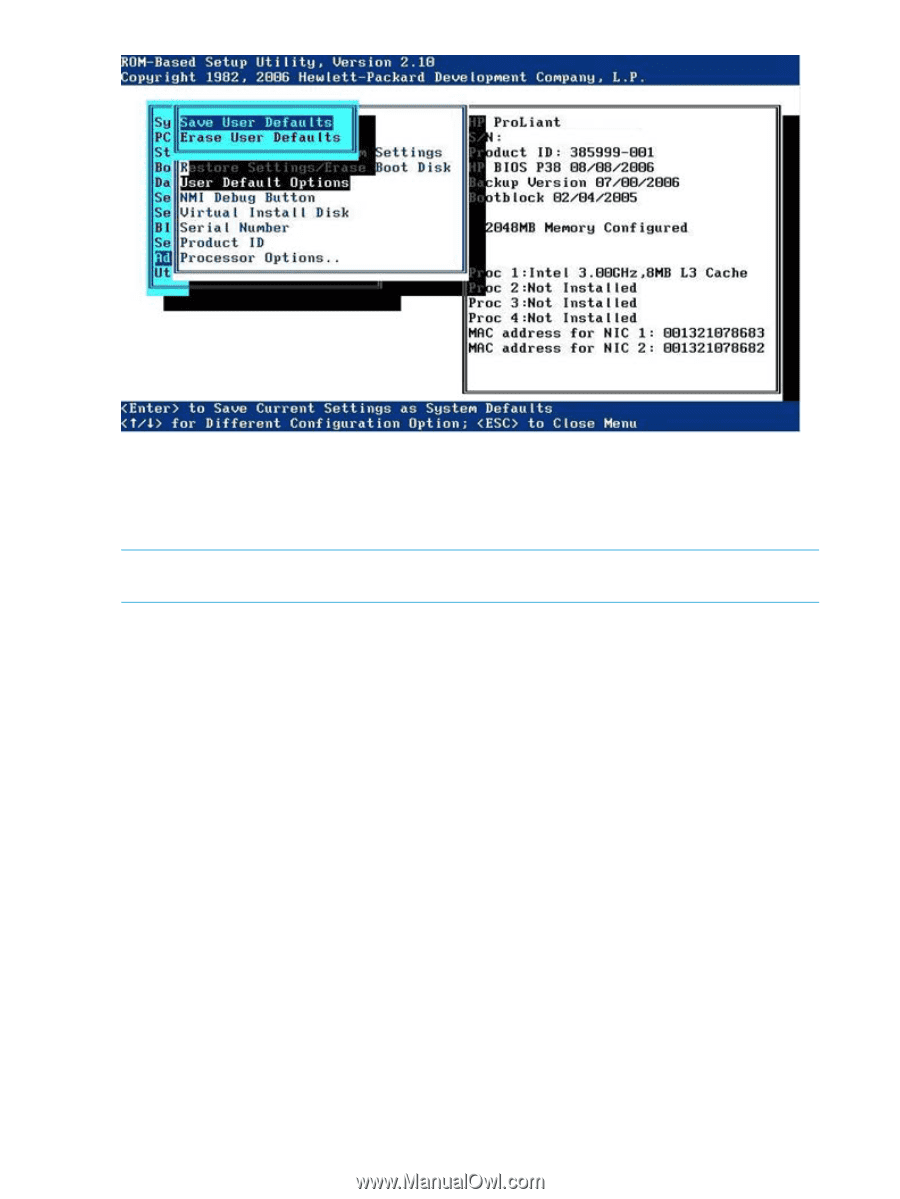
NMI Debug Button The NMI Debug Button option is a simple toggle setting that enables you to enable debug functionality when the system has experienced a software lock-up. The NMI Debug Button generates an NMI to allow the use of the OS debugger. NOTE: When enabled, pressing the NMI Debug Button on the system board during normal OS operation generates a Blue-Screen Trap, ABEND, or Panic, and halts the system. Virtual Install Disk The virtual install disk is a holding place within the system ROM that contains embedded boot drivers (such as SCSI or RAID controller drivers) that may be necessary to complete the operating system installation. Typically, boot drivers that are placed in the virtual install disk are either not included as part of the operating system media or are updated for new controllers. Supported operating systems automatically find these drivers, eliminating the need for user intervention. To further optimize the system, HP recommends updating these boot drivers to the latest version after the OS install. Secondary IDE Channel Support The Secondary IDE Channel Support option is a toggle setting that enables or disables the secondary IDE channel. When enabled, an additional IDE device can be connected to the secondary IDE channel. BIOS Enhanced RAID The BIOS Enhanced RAID feature is a toggle setting that, when enabled, analyzes the Linux data on installed hard drives for failure information. Based on the analysis, the system ROM automatically chooses which hard drive to boot. Node Interleaving The Node Interleaving feature requires all nodes to have equal memory sizes when enabled. Enabling Node Interleaving may affect OS performance. 184 RBSU menu-driven interface, version 2.xx (G5 and earlier servers)