Hitachi IC25N040ATCS04-0 Specifications - Page 119
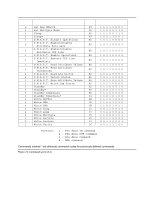
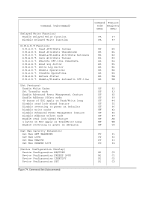
DMA Data Transfer commands
 |
UPC - 683728198664
View all Hitachi IC25N040ATCS04-0 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 119 highlights
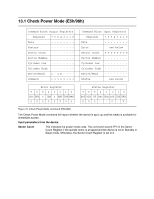
12.4 DMA Data Transfer commands These commands are: ! Read DMA ! Write DMA Data transfers using DMA commands differ in two ways from PIO transfers: ! Data transfers are performed using the Slave DMA channel ! No intermediate sector interrupts are issued on multisector commands Initiation of the DMA transfer commands is identical to the Read Sector or Write Sector commands with one exception: the host initializes the Slave DMA channel prior to issuing the command. The interrupt handler for DMA transfers differs in two ways: ! No intermediate sector interrupts are issued on multisector commands. ! The host resets the DMA channel prior to reading status from the device. The DMA protocol allows high performance multitasking operating systems to eliminate processor overhead associated with PIO transfers. 1. The host initializes the Slave DMA channel. 2. The host writes any required parameters to the Features, Sector Count, Sector Number, Cylinder, and Device/Head registers. 3. The host writes command code to the Command Register. 4. The device sets DMARQ when it is ready to transfer any part of the data. 5. The host transfers the data using the DMA transfer protocol currently in effect. 6. When all of the data has been transferred, the device generates an interrupt to the host. 7. The host resets the Slave DMA channel. 8. The host reads the Status Register and, optionally, the Error Register. Refer to section 7.0, "Electrical interface specifications" on page 41 for further details. Hitachi Travelstar 60GH & 40GN hard disk drive specifications 106