Netgear FVS318N FVS318 Reference Manual - Page 68
The FVS318 VPN tunnel, fields are defined in the following table., Table 6-1. - remote management
 |
View all Netgear FVS318N manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 68 highlights
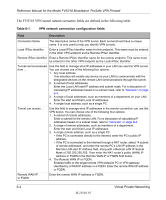
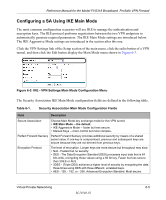
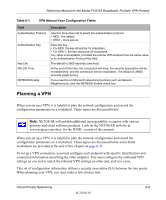
Reference Manual for the Model FVS318 Broadband ProSafe VPN Firewall The FVS318 VPN tunnel network connection fields are defined in the following table. Table 6-1. VPN network connection configuration fields Field Description Connection Name The descriptive name of the VPN tunnel. Each tunnel should have a unique name. It is only used to help you identify VPN tunnels. Local IPSec identifier Enter a Local IPSec Identifier name for this endpoint. This name must be entered in the other VPN endpoint as the Remote IPSec Identifier. Remote IPSec identifier Enter a Remote IPSec Identifier name for the remote endpoint. This name must be entered in the other VPN endpoint as the Local IPSec Identifier. Tunnel can be accessed Use this field to manage what IP addresses in your LAN can use this VPN tunnel. from ... You can choose one of the following four options: 1. Any local address. This selection will enable any device on your LAN to communicate with the designated devices on the remote LAN communications through this tunnel. 2. A subnet of local addresses. Enter the Local LAN start IP address and subnet mask. For a discussion of calculating IP addresses based on a subnet mask, refer to "Netmask" on page B-4. 3. A range of local addresses, such as members of a department on your LAN. Enter the start and finish Local IP addresses. 4. A single local address, such as a single PC. Tunnel can access ... Remote WAN IP or FQDN Use this field to manage what IP addresses in the remote connection can use this VPN tunnel. You can choose one of the following four options: 1. A subnet of remote addresses. Enter a subnet for the remote LAN. For a discussion of calculating IP addresses based on a subnet mask, refer to "Netmask" on page B-4. 2. A range of remote addresses, such as members of a department. Enter the start and finish Local IP addresses. 3. A single remote address, such as a single PC. • If the PC is connected directly to the Internet, enter the PC's public IP address. • If the PC is connected to the Internet through a NAT router, select "A subnet of remote addresses" and enter the remote PC's LAN IP address in the Remote LAN start IP Address field, along with a Remote LAN IP Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.255. Then enter the NAT router's public (WAN) IP address or FQDN in the Remote WAN IP or FQDN field below. 4. The Remote WAN IP or FQDN. Enables traffic to the target remote VPN endpoint PC or VPN gateway identified by a WAN IP address or a FQDN. Enter the remote WAN IP address or FQDN. Enter the remote WAN IP address or FQDN. 6-4 Virtual Private Networking M-10146-01