ZyXEL P-660HW-D1 v2 User Guide - Page 194
DiffServ
 |
View all ZyXEL P-660HW-D1 v2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 194 highlights
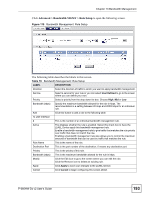
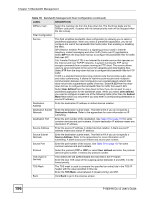
Chapter 13 Bandwidth Management 13.10 DiffServ DiffServ is a class of service (CoS) model that marks packets so that they receive specific perhop treatment at DiffServ-compliant network devices along the route based on the application types and traffic flow. Packets are marked with DiffServ Code Points (DSCPs) indicating the level of service desired. This allows the intermediary DiffServ-compliant network devices to handle the packets differently depending on the code points without the need to negotiate paths or remember state information for every flow. In addition, applications do not have to request a particular service or give advanced notice of where the traffic is going. 13.10.1 DSCP and Per-Hop Behavior DiffServ defines a new DS (Differentiated Services) field to replace the Type of Service (TOS) field in the IP header. The DS field contains a 2-bit unused field and a 6-bit DSCP field which can define up to 64 service levels. The following figure illustrates the DS field. DSCP is backward compatible with the three precedence bits in the ToS octet so that nonDiffServ compliant, ToS-enabled network device will not conflict with the DSCP mapping. Figure 111 DiffServ: Differentiated Service Field DSCP (6-bit) Unused (2-bit) The DSCP value determines the forwarding behavior, the PHB (Per-Hop Behavior), that each packet gets across the DiffServ network. Based on the marking rule, different kinds of traffic can be marked for different priorities of forwarding. Resources can then be allocated according to the DSCP values and the configured policies. PHB consists of two types of services: EF (Expedited Forwarding) and AF (Assured Forwarding). EF has higher priority. EF guarantees services with minimal loss and delay. AF has four sub-classes, each with three levels of importance (drop precedence). A high drop precedence means low importance. Table 77 Sub-Classes of AF Services DIFFSERV PRIORITY LOW DROP PRECEDENCE SUB-CLASS4 AF41 SUB-CLASS3 AF31 SUB-CLASS2 AF21 SUB-CLASS1 AF11 MEDIUM DROP PRECEDENCE AF42 AF32 AF22 AF12 HIGH DROP PRECEDENCE AF43 AF33 AF23 AF13 13.10.2 Rule Configuration Click the Edit icon or select User Defined from the Service drop-down list in the Rule Setup screen to configure a bandwidth management rule. Use bandwidth rules to allocate specific amounts of bandwidth capacity (bandwidth budgets) to specific applications and/or subnets. 194 P-660HW-Dx v2 User's Guide