ZyXEL P-660RU-T1 v3s User Guide - Page 101
Quality of Service (QoS), 11.1 Overview
 |
View all ZyXEL P-660RU-T1 v3s manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 101 highlights
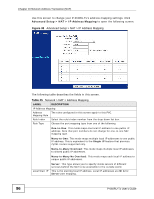
CHAPTER 11 Quality of Service (QoS) 11.1 Overview Use the QoS screen to set up your P-660RU-Tx to use QoS for traffic management. Quality of Service (QoS) refers to both a network's ability to deliver data with minimum delay, and the networking methods used to control bandwidth. QoS allows the P-660RU-Tx to group and prioritize application traffic and fine-tune network performance. Without QoS, all traffic data are equally likely to be dropped when the network is congested. This can cause a reduction in network performance and make the network inadequate for time-critical applications such as video-on-demand. The P-660RU-Tx assigns each packet a priority and then queues the packet accordingly. Packets assigned with a high priority are processed more quickly than those with low priorities if there is congestion, allowing time-sensitive applications to flow more smoothly. Time-sensitive applications include both those that require a low level of latency (delay) and a low level of jitter (variations in delay) such as Voice over IP (VoIP) or Internet gaming, and those for which jitter alone is a problem such as Internet radio or streaming video. In the following figure, your Internet connection has an upstream transmission speed of 50 Mbps. You configure a classifier to assign the highest priority queue (6) to VoIP traffic from the LAN interface, so that voice traffic would not get delayed when there is network congestion. Traffic from the boss's IP address (192.168.1.23 for example) is mapped to queue 5. Traffic that does not match P-660RU-Tx User's Guide 101