ZyXEL P-660RU-T1 v3s User Guide - Page 94
Configuring the Virtual Server Screen, Table 24
 |
View all ZyXEL P-660RU-T1 v3s manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 94 highlights
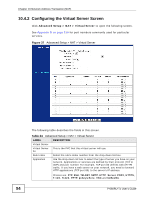
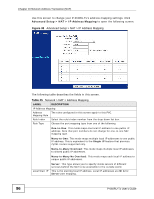
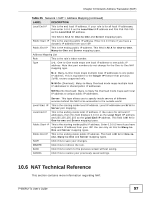
Chapter 10 Network Address Translation (NAT) 10.4.2 Configuring the Virtual Server Screen Click Advanced Setup > NAT > Virtual Server to open the following screen. See Appendix D on page 219 for port numbers commonly used for particular services. Figure 37 Advanced Setup > NAT > Virtual Server The following table describes the fields in this screen. Table 24 Advanced Setup > NAT > Virtual Server LABEL DESCRIPTION Virtual Server Virtual Server This is the PVC that this virtual server will use. for Rule Index Select the rule's index number from the drop-down list box. Application Use the drop-down list box to select the type of server you have on your network. Applications or services are defined by their protocol (TCP or UDP) and port number. For example, TCP port 80 defines web (HTTP) traffic. If you have a web server on your network, you need to forward HTTP applications (TCP port 80) to the server's IP address. Choices are: FTP, SSH, TELNET, SMTP, HTTP_Server, POP3, HTTPS, T.120, H.323, PPTP, pcAnywhere, VNC and CUSeeMe. 94 P-660RU-Tx User's Guide