Kyocera ECOSYS FS-4100DN PRESCRIBE Commands Technical Reference Manual - Rev. - Page 49
Printout of the PCRP Example, Second PCRP Example, R! RES; UNIT C; NEWP; SPD .1, PMZP 3
 |
View all Kyocera ECOSYS FS-4100DN manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
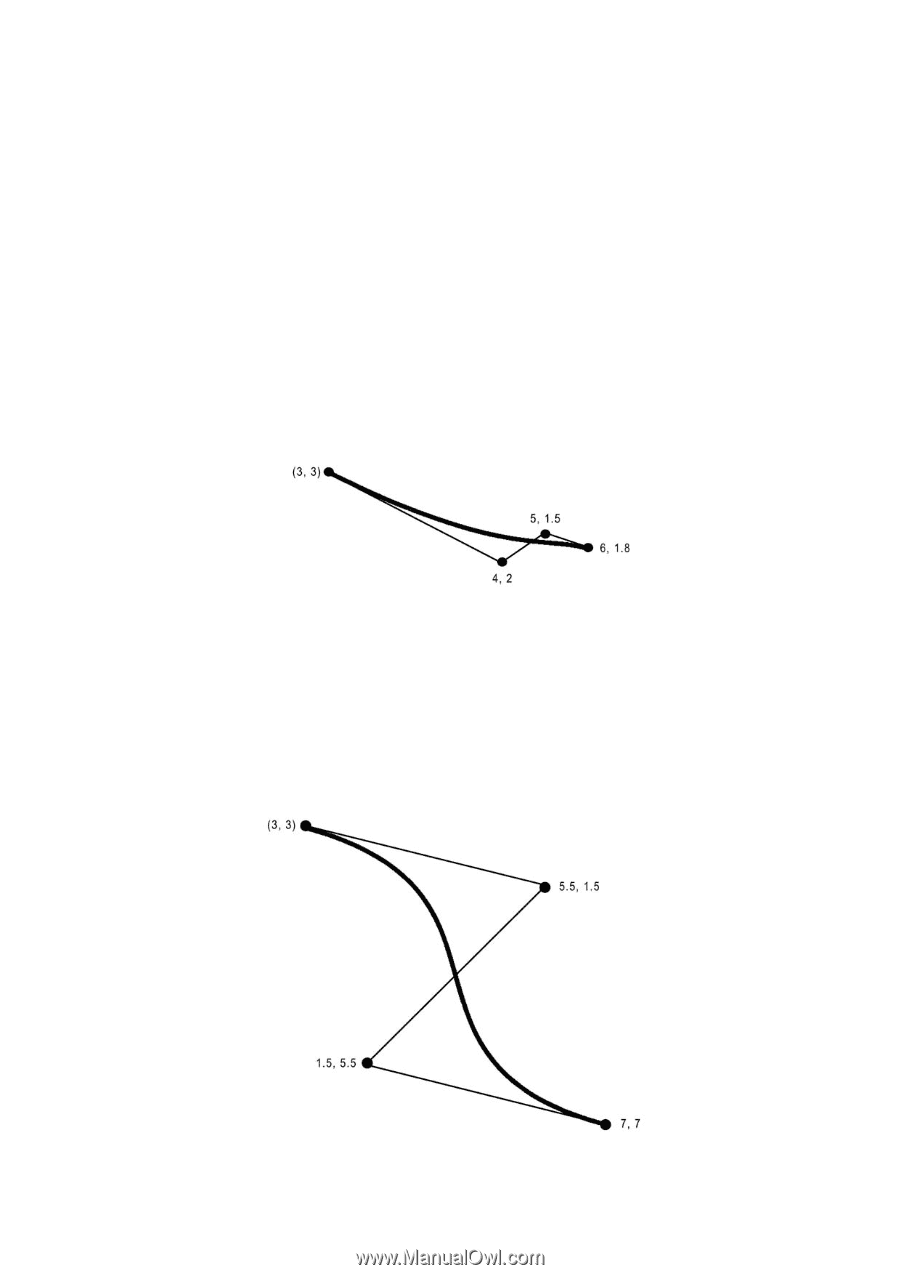
Path Mode Graphics The curve leaves the current position in the direction of x1, y1, and is tangent to the line between the current position and x1, y1. It bends towards x2, y2, then to x3, y3, and at the end point, is tangent to the line between x2, y2 and x3, y3. The curve is always entirely enclosed by the complex quadrilateral defined by the starting point, x1, y1, x2, y2, and x3, y3. See the following examples: !R! RES; UNIT C; NEWP; SPD .1; PMZP 3, 3; PCRP 4, 2, 5, 1.5, 6, 1.8; STRK; PAGE; EXIT; Figure 2. 26. Printout of the PCRP Example !R! RES; UNIT C; NEWP; SPD .1; PMZP 3, 3; PCRP 5.5, 1.5, 1.5, 5.5, 7, 7; STRK; PAGE; EXIT; Figure 2. 27. Second PCRP Example 2-27
Path Mode Graphics
2-27
The curve leaves the current position in the direction of
x1, y1,
and is tangent to the line
between the current position and
x1, y1
. It bends towards
x2, y2
, then to
x3, y3
, and at the
end point, is tangent to the line between x2, y2 and x3, y3. The curve is always entirely
enclosed by the complex quadrilateral defined by the starting point,
x1, y1, x2, y2
, and
x3, y3.
See the following examples:
!R! RES; UNIT C; NEWP; SPD .1;
PMZP 3, 3;
PCRP 4, 2, 5, 1.5, 6, 1.8;
STRK;
PAGE;
EXIT;
Figure 2. 26.
Printout of the PCRP Example
!R! RES; UNIT C; NEWP; SPD .1;
PMZP 3, 3;
PCRP 5.5, 1.5, 1.5, 5.5, 7, 7;
STRK;
PAGE;
EXIT;
Figure 2. 27.
Second PCRP Example