D-Link DWL-8500AP Product Manual - Page 51
WPA Personal Configuration, WPA Personal, WPA Versions, WPA2., WPA and WPA2., Cipher
 |
UPC - 790069297212
View all D-Link DWL-8500AP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 51 highlights
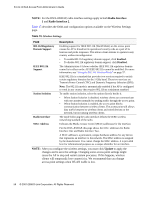
4 Configuring Access Point Security PSK is used for an initial check of credentials only. This security mode is backwardscompatible for wireless clients that support the original WPA. If you select WPA Personal as the Security Mode, additional fields display, as Figure 12 shows. Figure 12. WPA Personal Configuration Table 13 describes the configuration options for the WPA Personal security mode. Table 13. WPA Personal Field Description WPA Versions Select the types of client stations you want to support: • WPA. If all client stations on the network support the original WPA but none support the newer WPA2, then select WPA. • WPA2. If all client stations on the network support WPA2, we suggest using WPA2 which provides the best security per the IEEE 802.11i standard. • WPA and WPA2. If you have a mix of clients, some of which support WPA2 and others which support only the original WPA, select both of the check boxes. This lets both WPA and WPA2 client stations associate and authenticate, but uses the more robust WPA2 for clients who support it. This WPA configuration allows more interoperability, at the expense of some security. Cipher Suites Select the cipher suite you want to use: • TKIP • CCMP (AES) • TKIP and CCMP (AES) Both TKIP and AES clients can associate with the access point. WPA clients must have one of the following to be able to associate with the AP: • A valid TKIP key • A valid AES-CCMP key Clients not configured to use WPA Personal will not be able to associate with the AP. Key The pre-shared key is the shared secret key for WPA Personal. Enter a string of at least 8 characters to a maximum of 63 characters. NOTE: After you configure the security settings, you must click Update to apply the changes and to save the settings. Changing some access point settings might cause the AP to stop and restart system processes. If this happens, wireless clients will temporarily lose connectivity. We recommend that you change access point settings when WLAN traffic is low. Configuring Virtual Access Point Security 51