D-Link DWL-8500AP Product Manual - Page 60
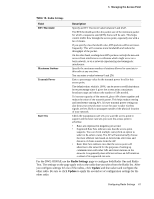
Beacon Interval, DTIM Period, Fragmentation, Threshold, Radio Settings, Table 16., Field, Description
 |
UPC - 790069297212
View all D-Link DWL-8500AP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 60 highlights
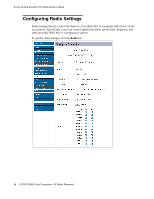
D-Link Unified Access Point Administrator's Guide Table 16. Radio Settings Field Beacon Interval DTIM Period Fragmentation Threshold Description Enter a value from 20 to 2000 milliseconds. Beacon frames are transmitted by an access point at regular intervals to announce the existence of the wireless network. The default behavior is to send a beacon frame once every 100 milliseconds (or 10 per second). Specify a DTIM period from 1-255 beacons. The Delivery Traffic Information Map (DTIM) message is an element included in some Beacon frames. It indicates which client stations, currently sleeping in low-power mode, have data buffered on the access point awaiting pick-up. The DTIM period you specify indicates how often the clients served by this access point should check for buffered data still on the AP awaiting pickup. The measurement is in beacons. For example, if you set this field to 1, clients will check for buffered data on the AP at every beacon. If you set this field to 10, clients will check on every 10th beacon. Specify a number between 256 and 2,346 to set the frame size threshold in bytes. The fragmentation threshold is a way of limiting the size of frames transmitted over the network. If a packet exceeds the fragmentation threshold, the fragmentation function is activated and the packet is sent as multiple 802.11 frames. If the packet being transmitted is equal to or less than the threshold, fragmentation is not used. Setting the threshold to the largest value (2,346 bytes) effectively disables fragmentation. Fragmentation involves more overhead both because of the extra work of dividing up and reassembling of frames it requires, and because it increases message traffic on the network. However, fragmentation can help improve network performance and reliability if properly configured. Sending smaller frames (by using lower fragmentation threshold) might help with some interference problems; for example, it might help with microwave oven interference. By default, fragmentation is off. We recommend not using fragmentation unless you suspect radio interference. The additional headers applied to each fragment increase the overhead on the network and can greatly reduce throughput. 60 © 2001-2008 D-Link Corporation. All Rights Reserved.