Fujitsu MHT2030AT Manual/User Guide - Page 187
PIO Data transferring commands from host to device, Number, Cylinder, and Device/Head registers.
 |
UPC - 683728090579
View all Fujitsu MHT2030AT manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 187 highlights
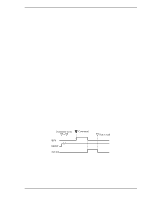
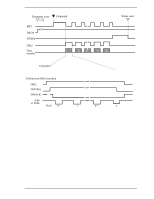
5.4 Command Protocol 5.4.2 PIO Data transferring commands from host to device The execution of the following commands involves Data transfer from the host to the drive. • WRITE SECTOR(S) (EXT) • WRITE LONG • WRITE BUFFER • WRITE VERIFY • SMART WRITE LOG SECTOR • SECURITY DISABLE PASSWORD • SECURITY ERASE UNIT • SECURITY SET PASSWORD • SECURITY UNCLOK The execution of these commands includes the transfer one or more sectors of data from the host to the device. In the WRITE LONG command, 516 bytes are transferred. Following shows the protocol outline. a) The host writes any required parameters to the Features, Sector Count, Sector Number, Cylinder, and Device/Head registers. b) The host writes a command code in the Command register. The drive sets the BSY bit of the Status register. c) When the device is ready to receive the data of the first sector, the device sets DRQ bit and clears BSY bit. d) The host writes one sector of data through the Data register. e) The device clears the DRQ bit and sets the BSY bit. f) When the drive completes transferring the data of the sector, the device clears BSY bit and asserts INTRQ signal. If transfer of another sector is requested, the drive sets the DRQ bit. g) After detecting the INTRQ signal assertion, the host reads the Status register. h) The device resets INTRQ (the interrupt signal). i) If transfer of another sector is requested, steps d) and after are repeated. Figure 5.5 shows an example of WRITE SECTOR(S) command protocol. C141-E192-02EN 5-113