Fujitsu MHT2030AT Manual/User Guide - Page 64
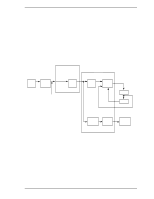
Digital PLL circuit
 |
UPC - 683728090579
View all Fujitsu MHT2030AT manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 64 highlights
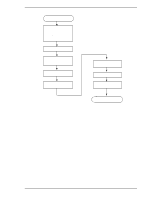
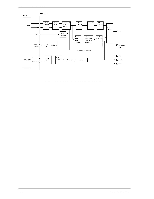
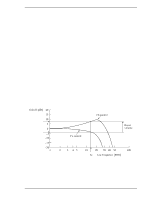
Theory of Device Operation (3) FIR circuit This circuit is 10-tap sampled analog transversal filter circuit that equalizes the head read signal to the Modified Extended Partial Response (MEEPR) waveform. (4) A/D converter circuit This circuit changes Sampled Read Data Pulse from the FIR circuit into Digital Read Data. (5) Viterbi detection circuit The sample hold waveform output from the flash digitizer circuit is sent to the Viterbi detection circuit. The Viterbi detection circuit demodulates data according to the survivor path sequence. (6) ENDEC This circuit converts the read data into the NRZ data. 4.6.4 Digital PLL circuit The drive uses constant density recording to increase total capacity. This is different from the conventional method of recording data with a fixed data transfer rate at all data area. In the constant density recording method, data area is divided into zones by radius and the data transfer rate is set so that the recording density of the inner cylinder of each zone is nearly constant. The drive divides data area into 30 zones to set the data transfer rate. The MPU transfers the data transfer rate setup data (SD/SC) to the RDC that includes the Digital PLL circuit to change the data transfer rate. 4-12 C141-E192-02EN