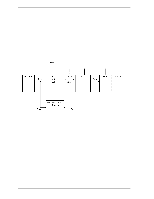Fujitsu MHT2030AT Manual/User Guide - Page 61
Command processing during self-calibration, 4.6 Read/write Circuit
 |
UPC - 683728090579
View all Fujitsu MHT2030AT manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 61 highlights
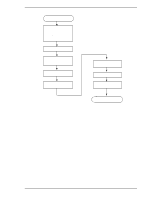
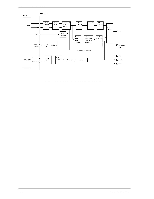
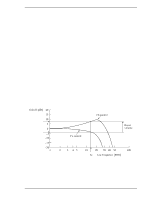
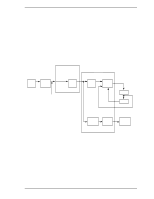
4.6 Read/write Circuit 4.5.3 Command processing during self-calibration This enables the host to execute the command without waiting for a long time, even when the disk drive is performing self-calibration. The command execution wait time is about maximum 72 ms. When the error rate of data reading, writing, or seeking becomes lower than the specified value, self-calibration is performed to maintain disk drive stability. If the disk drive receives a command execution request from the host while performing self-calibration, it stops the self-calibration and starts to execute the command. In other words, if a disk read or write service is necessary, the disk drive positions the head to the track requested by the host, reads or writes data, and then restarts calibration after about 3 seconds. If the error rate recovers to a value exceeding the specified value, self-calibration is not performed. 4.6 Read/write Circuit The read/write circuit consists of the read/write preamplifier (PreAMP), the write circuit, the read circuit, and the time base generator in the read channel (RDC). Figure 4.4 is a block diagram of the read/write circuit. 4.6.1 Read/write preamplifier (PreAMP) PreAMP equips a read preamplifier and a write current switch, that sets the bias current to the MR device and the current in writing. Each channel is connected to each data head, and PreAMP switches channel by serial I/O. In the event of any abnormalities, including a head short-circuit or head open circuit, the write unsafe signal is generated so that abnormal write does not occur. 4.6.2 Write circuit The write data is output from the hard disk controller (HDC) with the NRZ data format, and sent to the encoder circuit in the RDC. The NRZ write data is converted to RLL (Run Length Limited) code data by the encoder circuit then sent to the PreAMP, and the data is written onto the media. (1) RLL code MEEPRML This device converts data using the RLL (Run Length Limited) algorithm. (2) Write precompensation Write precompensation compensates, during a write process, for write nonlinearity generated at reading. C141-E192-02EN 4-9