HP Indigo 7000 User Guide 2 - Page 253
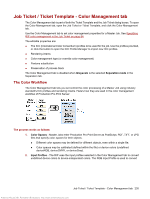
Job Ticket / Ticket Template - Color Management tab
 |
View all HP Indigo 7000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 253 highlights
Gray input profile Sets the input profile for any color represented as grayscale. The HP Production RIP converts grayscale colors to device-independent colors according to the transform in the profile, then re-separates the colors into CMYK for the press using the current press output profile and rendering intent. Choosing None, the default, causes grayscale data to be treated as black CMYK data. There are no preloaded input profiles. To add input profiles, use the ICC Profile Manager. Press output profiles Sets the press output profile. On the HP Indigo press, it is not necessary to change the output profile for gloss, semi-matte, and matte media because the press compensates for the media automatically by using different calibration values for the ink 100% optical density. Emulation profile Enables reproduction of the color characteristics of another device with a smaller gamut. Emulation profiles allow simulation of not only CMYK data, but also RGB and other colormanaged colors. When an emulation profile is used, the media color specified by the profile is also simulated. The current CMYK rendering intent choice is used for the color transformations into the Emulation color space, but Absolute colorimetric is always used for the conversions from the emulation space through the press output profile. If this behavior is not desired, the emulation can be created for CMYK data by assigning the profile as a CMYK Input Profile instead of as an emulation profile. In the Emulation profile list on the Color Management tab, None is the default, and there are no profiles loaded. To add emulation profiles, use the ICC Profile Manager. CMYK input profiles may be imported as emulation profiles with the ICC Profile Manager. ICC Profile Manager Click to open a window for adding input profiles, emulation profiles, and output profiles. Rendering intent Sets the job's rendering intent, an adjustment of its print qualities based on the needs of the job. The list includes the four standard ICC rendering intents: ● Perceptual - best for good reproduction of images and all RGB inputs. ● Saturation - intended to be used for colorful business graphics where accuracy is not as important as color saturation. ● Relative Colorimetric - best for proofing or accurate color reproduction of CMYK colors. If this intent is used for RGB content or with non-gloss media, Blackpoint compensation may be required for optimal results. ● Absolute Colorimetric - similar to relative colorimetric except that color can be added to "white" areas to simulate the media color defined in the input profile. CMYK image rendering intent Allows you to set the rendering intent for a Master Job's CMYK images separately from the job's rendering intent. If a CMYK image intent is specified, it overrides the default rendering intent for CMYK images. RGB image rendering intent Allows you to set the rendering intent for a Master Job's RGB images separately from the job's rendering intent. Recommended when the Relative Colorimetric intent is chosen for the job, but documents may contain RGB data that require Perceptual intent. Use Black Point Compensation Affects the relative colorimetric rendering intent only. It causes the RIP color management engine to normalize the black points of the input and output profiles, mapping input black to output black. This is useful for color management of RGB content as well as Matte and uncoated media. In these cases, the press output black can be lighter than the input black. With the relative colorimetric intent, the black is preserved causing the dark shadows and near blacks to block up when the input is darker than the output can reproduce. Blackpoint compensation scales the lightness of the images to normalize the black points to eliminate this effect. Pantone colors can be emulated using the wide gamut of the Indichrome ink set using the Pantone licensed lookup table. In addition, there are four Pantone Emulation options for simulating Pantone colors with CMYK inks: HP Professional Pantone Emulation Converts named Pantone colors in the job file to process CMYK values using a special HP-proprietary form of gamut mapping. This method provides a "best visual match" on the press for each individual Pantone color. This method uses the Pantone name suffix to differentiate between the Pantone Coated, Matte and Uncoated libraries. This method is good at matching the individual Pantone colors. Job Ticket / Ticket Template - Color Management tab 237 Antenna House XSL Formatter (Evaluation) http://www.antennahouse.com/