HP t530 Hardware Reference Guide - Page 48
Japanese power cord requirements, Country-specific requirements, Statement of Volatility
 |
View all HP t530 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 48 highlights
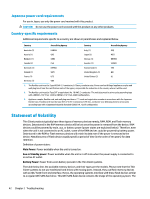
Japanese power cord requirements For use in Japan, use only the power cord received with this product. CAUTION: Do not use the power cord received with this product on any other products. Country-specific requirements Additional requirements specific to a country are shown in parentheses and explained below. Country Accrediting Agency Country Accrediting Agency Australia (1) Austria (1) Belgium (1) Canada (2) EANSW OVE CEBC CSA Italy (1) Japan (3) Norway (1) Sweden (1) IMQ METI NEMKO SEMKO Denmark (1) Finland (1) France (1) Germany (1) DEMKO SETI UTE VDE Switzerland (1) SEV United Kingdom (1) BSI United States (2) UL 1. The flexible cord must be Type HO5VV-F, 3-conductor, 0.75mm2 conductor size. Power cord set fittings (appliance coupler and wall plug) must bear the certification mark of the agency responsible for evaluation in the country where it will be used. 2. The flexible cord must be Type SVT or equivalent, No. 18 AWG, 3-conductor. The wall plug must be a two-pole grounding type with a NEMA 5-15P (15A, 125V) or NEMA 6-15P (15A, 250V) configuration. 3. Appliance coupler, flexible cord, and wall plug must bear a "T" mark and registration number in accordance with the Japanese Dentori Law. Flexible cord must be Type VCT or VCTF, 3-conductor, 0.75 mm2 conductor size. Wall plug must be a two-pole grounding type with a Japanese Industrial Standard C8303 (7A, 125V) configuration. Statement of Volatility Thin Client products typically have three types of memory devices namely, RAM, ROM, and Flash memory devices. Data stored in the RAM memory device will be lost once the power is removed from the device. RAM devices could be powered by main, aux, or battery power (power states are explained below). Therefore, even when the unit is not connected to an AC outlet, some of the RAM devices could be powered by battery power. Data stored in the ROM or Flash memory devices will retain its data even if the power is removed to the device. Manufacturers of Flash device usually specify a period of time (in the order of ten years) for data retention. Definition of power states: Main Power: Power available when the unit is turned on. Aux or Standby power: Power available when the unit is in off state when the power supply is connected to an active AC outlet. Battery Power: Power from a coin battery present in the Thin Client systems. The table below lists the available memory devices and their types per the models. Please note that the Thin Client systems do not use traditional hard drives with moving parts. Instead, they use flash memory devices with an IDE/ SATA front-end interface. Hence, the operating systems interface with these flash devices similar to a regular IDE/ SATA hard drive. This IDE/ SATA flash device contains the image of the operating system. The 42 Chapter 2 Troubleshooting