Hitachi HTS541680J9AT00 Specifications - Page 77
Protected Area Function
 |
UPC - 683728200794
View all Hitachi HTS541680J9AT00 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 77 highlights
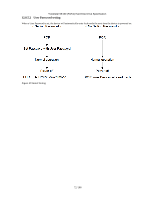
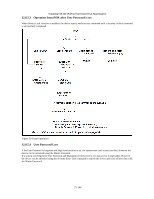
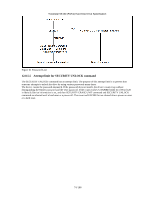
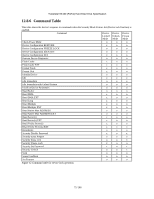
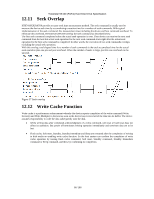
12.9 Travelstar 5K160 (PATA) Hard Disk Drive Specification Protected Area Function Protected Area Function is to provide the 'protected area' which can not be accessed via conventional method. This 'protected area' is used to contain critical system data such as BIOS or system management information. The contents of entire system main memory may also be dumped into 'protected area' to resume after system power off. The LBA/CYL changed by following command affects the Identify Device Information. Two commands are defined for this function. Read Native Max ADDRESS ('F8'h) Set Max ADDRESS ('F9'h) Four security extension commands are implemented as sub-functions of the Set Max ADDRESS. Set Max SET PASSWORD Set Max LOCK Set Max FREEZE LOCK Set Max UNLOCK 12.9.1 Example for operation (In LBA mode) Assumptions : For better understanding, the following example uses actual values for LBA, size, etc. Since it is just an example, these values could be different. Device characteristics Capacity (native) : 536,870,912 byte (536MB) Max LBA (native) : 1,048,575 (0FFFFFh) Required size for protected area : 8,388,608 byte Required blocks for protected area : 16,384 (004000h) Customer usable device size : 528,482,304 byte (528MB) Customer usable sector count : 1,032,192 (0FC000h) LBA range for protected area : 0FC000h to 0FFFFFh 1. Shipping HDDs from HDD manufacturer When the HDDs are shipped from HDD manufacturer, the device has been tested to have a capacity of 536MB,flagging the media defects not to be visible by system. 2. Preparing HDDs at system manufacturer Special utility software is required to define the size of protected area and store the data into it. The sequence is : Issue Read Native Max ADDRESS command to get the real device max of LBA/CYL. Returned value shows that native device Max LBA is 0FFFFFh regardless to the current setting. Make entire device be accessible including the protected area by setting device Max LBA as 0FFFFFh via Set Max ADDRESS command. The option could be either nonvolatile or volatile. Test the sectors for protected area (LBA >= 0FC000h) if required. Write information data such as BIOS code within the protected area. Change maximum LBA using Set Max ADDRESS command to 0FBFFFh with nonvolatile option. From this point, the protected area cannot be accessed until next Set Max ADDRESS command is issued. Any BIOSes, device drivers, or application software access the HDD as if that is the 528MB device because the device acts exactly same as real 528MB device does. 3. Conventional usage without system software support Since the HDD works as 528MB device, there is no special care to use this device for normal use. 4. Advanced usage using protected area The data in the protected area is accessed by following. Issue Read Native Max ADDRESS command to get the real device max LBA/CYL. Returned value shows that native device Max LBA is 0FFFFFh regardless of the current setting. Make entire device be accessible including the protected area by setting device Max LBA as 0FFFFFh via Set Max ADDRESS command with volatile option. By using this option, unexpected power removal or reset will not make the protected area remained accessible. Read information data from protected area. Issue hard reset or POR to inhibit any access to the protected area. 77/188