Intel S1200RP Technical Product Specification - Page 65
Dedicated Management Channel, 11.3.2.3, Concurrent Server Management Use of Multiple
 |
View all Intel S1200RP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 65 highlights
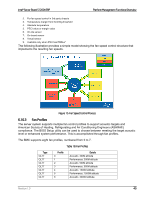
Intel® Server Board S1200V3RP Platform Management Functional Overview The baseboard NICs are connected to a single BMC RMII/RGMII port that is configured for RMII operation. The NC-SI protocol is used for this connection and provides a 100 Mb/s full-duplex multi-drop interface which allows multiple NICs to be connected to the BMC. The physical layer is based upon RMII, however RMII is a point-to-point bus whereas NC-SI allows 1 master and up to 4 slaves. The logical layer (configuration commands) is incompatible with RMII. The server board provides support for a dedicated management channel that can be configured to be hidden from the host and only used by the BMC. This mode of operation is configured using a BIOS setup option. 6.11.3.2.2 Dedicated Management Channel An additional LAN channel dedicated to BMC usage and not available to host SW is supported using an optional RMM4 add-in card. There is only a PHY device present on the RMM4 add-in card. The BMC has a built-in MAC module that uses the RGMII interface to link with the card's PHY. Therefore, for this dedicated management interface, the PHY and MAC are located in different devices. The PHY on the RMM4 connects to the BMC's other RMII/RGMII interface (that is, the one that is not connected to the baseboard NICs). This BMC port is configured for RGMII usage. In addition to the use of an RMM4 add-in card for a dedicated management channel, on systems that support multiple Ethernet ports on the baseboard, the system BIOS provides a setup option to allow one of these baseboard ports to be dedicated to the BMC for manageability purposes. When this is enabled, that port is hidden from the OS. 6.11.3.2.3 Concurrent Server Management Use of Multiple Ethernet Controllers The BMC FW supports concurrent OOB LAN management sessions for the following combination: 2 on-board NIC ports 1 on-board NIC and the optional dedicated RMM4 add-in management NIC 2 on-board NICs and optional dedicated RMM4 add-in management NIC All NIC ports must be on different subnets for the concurrent usage models above. MAC addresses are assigned for management NICs from a pool of up to 3 MAC addresses allocated specifically for manageability. The server board has seven MAC addresses programmed at the factory. MAC addresses are assigned as follows: NIC 1 MAC address (for OS usage) NIC 2 MAC address = NIC 1 MAC address + 1 (for OS usage) BMC LAN channel 1 MAC address = NIC1 MAC address + 2 BMC LAN channel 2 MAC address = NIC1 MAC address + 3 BMC LAN channel 3 (RMM) MAC address = NIC1 MAC address + 4 Revision 1.0 53