Netgear FSM726S FSM726S User Manual - Page 21
of 110
 |
UPC - 606449023091
View all Netgear FSM726S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
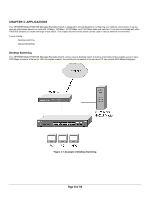
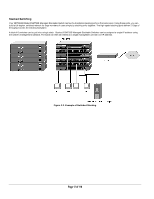
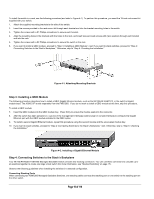
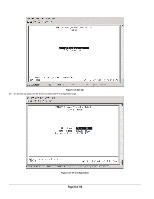
After you power-up the switch for the first time, you can configure it using a VT100/ANSI terminal or a PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation that is directly connected to the switch's console port. Thereafter, you can assign an IP address, subnet mask, and gateway address to the switch and manage it through a Web browser, Telnet session, or SNMP management application. For more information about using the console, see Chapter 6, Administration Console Access. To connect a console to the switch: 15. Connect a VT100/ANSI terminal or a PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation to the switch's console port, labeled Console, using the null- modem cable supplied with the switch. The supplied null-modem cable has 9-pin connectors on each end. Note: you must connect the console cable to the master switch. Connecting the console cable a slave switch will not allow configuration Note: If you are stacking your switches, you only have to configure the Master unit via the Console port. Once you have assigned an IP address to the master unit, you can use the browser interface to configure the other units. 16. If you attached a PC, Apple Macintosh, or UNIX workstation, start a terminal-emulation program. Microsoft Windows users can use HyperTerminal, which comes with the Windows operating systems. Macintosh users can use ZTerm. UNIX users can use a terminal emulator such as TIP. 17. Configure the terminal-emulation program to use the following settings: Baud rate: 9,600 bps Data bits: 8 Parity: none Stop bit: 1 Flow control: none Page 21 of 110