Netgear RN526X Software Manual - Page 164
Con Bonded Adapters, Teaming Modes, Hash Types
 |
View all Netgear RN526X manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 164 highlights
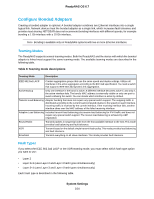
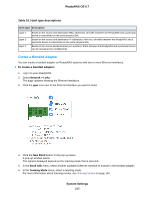
ReadyNAS OS 6.7 Configure Bonded Adapters Creating a bonded adapter is optional. A bonded adapter combines two Ethernet interfaces into a single logical link. Network devices treat the bonded adapter as a single link, which increases fault tolerance and provides load sharing. NETGEAR does not recommend bonding interfaces with different speeds, for example bonding a 1 Gb interface with a 10 Gb interface. Note Bonding is available only on ReadyNAS systems with two or more Ethernet interfaces. Teaming Modes The ReadyNAS supports several teaming modes. Both the ReadyNAS and the device with which the bonded adapter is linked must support the same teaming mode. The available teaming modes are described in the following table. Table 9. Teaming mode descriptions Teaming Mode Description IEEE 802.3ad LACP Creates aggregation groups that use the same speed and duplex settings. Utilizes all interfaces in the active aggregator according to the 802.3ad specification.You need a switch that supports IEEE 802.3ad dynamic link aggregation. Active Backup Only one interface in the bond is active. A different interface becomes active if, and only if, the active interface fails. The bond's MAC address is externally visible on only one port to avoid confusing the switch. You can decide which interface is active by default. Transmit Load Balancing Adapter bonding that does not require any special switch support. The outgoing traffic is distributed according to the current load (computed relative to the speed) on each interface. Incoming traffic is received by the current interface. If the receiving interface fails, another interface takes over the MAC address of the failed receiving interface. Adaptive Load Balancing Includes transmit load balancing plus receive load balancing for IPV4 traffic and does not require any special switch support. The receive load balancing is achieved by ARP negotiation. Round-Robin Transmit packets in sequential order from the first available interface to the next. This mode provides load balancing and fault tolerance. XOR Transmit based on the default simple transmit hash policy.This mode provides load balancing and fault tolerance. Broadcast Transmit everything on all slave interfaces. This mode provides fault tolerance. Hash Types If you select the IEEE 802.3ad LACP or the XOR teaming mode, you must select which hash type option you want to use: • Layer 2 • Layer 2+3 (uses Layer 2 and Layer 3 hash types simultaneously) • Layer 3+4 (uses Layer 3 and Layer 4 hash types simultaneously) Each hash type is described in the following table. System Settings 164