HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches ACL and QoS Command Refere - Page 23
rule (IPv4 advanced ACL view), Examples, Syntax, Default level, Parameters
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 23 highlights
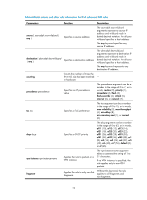
NOTE: The lsap keyword is not supported if the ACL is for QoS traffic classification or packet filtering. Examples # Create a rule in ACL 4000 to permit ARP packets and deny RARP packets. system-view [Sysname] acl number 4000 [Sysname-acl-ethernetframe-4000] rule permit type 0806 ffff [Sysname-acl-ethernetframe-4000] rule deny type 8035 ffff rule (IPv4 advanced ACL view) Syntax rule [ rule-id ] { deny | permit } protocol [ { { ack ack-value | fin fin-value | psh psh-value | rst rst-value | syn syn-value | urg urg-value } * | established } | counting | destination { dest-addr dest-wildcard | any } | destination-port operator port1 [ port2 ] | dscp dscp | fragment | icmp-type { icmp-type [ icmp-code ] | icmp-message } | precedence precedence | source { sour-addr sour-wildcard | any } | source-port operator port1 [ port2 ] | time-range time-range-name | tos tos | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name ] * View undo rule rule-id [ { { ack | fin | psh | rst | syn | urg } * | established } | counting | destination | destination-port | dscp | fragment | icmp-type | precedence | source | source-port | time-range | tos | vpn-instance ] * IPv4 advanced ACL view Default level 2: System level Parameters rule-id: Specifies a rule ID, in the range of 0 to 65534. If no rule ID is provided when you create an ACL rule, the system automatically assigns it a rule ID. This rule ID takes the nearest higher multiple of the numbering step to the current highest rule ID, starting from 0. For example, if the rule numbering step is 5 and the current highest rule ID is 28, the rule is numbered 30. deny: Denies matching packets. permit: Allows matching packets to pass. protocol: Protocol carried by IPv4. It can be a number in the range of 0 to 255, or in words, gre (47), icmp (1), igmp (2), ip, ipinip (4), ospf (89), tcp (6), or udp (17). Table 6 describes the parameters that you can specify regardless of the value that the protocol argument takes. 18