HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches ACL and QoS Command Refere - Page 29
rule (IPv6 advanced ACL view
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
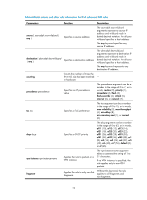
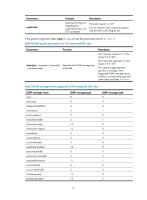
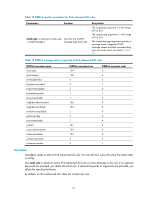
Within an ACL, the permit or deny statement of each rule must be unique. If the ACL rule you are creating or editing has the same deny or permit statement as another rule in the ACL, your creation or editing attempt will fail. To view rules in an ACL and their rule IDs, use the display acl all command. Related commands: acl, display acl, step, and time-range. NOTE: • If an IPv4 basic ACL is for QoS traffic classification, do not specify the vpn-instance keyword, and the counting keyword (even if specified) does not take effect for QoS. • If an IPv4 basic ACL is for packet filtering, do not specify the vpn-instance keyword. Examples # Create a rule in IPv4 basic ACL 2000 to deny the packets from any source IP segment but 10.0.0.0/8, 172.17.0.0/16, or 192.168.1.0/24. system-view [Sysname] acl number 2000 [Sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule permit source 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 [Sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule permit source 172.17.0.0 0.0.255.255 [Sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule permit source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 [Sysname-acl-basic-2000] rule deny source any rule (IPv6 advanced ACL view) Syntax rule [ rule-id ] { deny | permit } protocol [ { { ack ack-value | fin fin-value | psh psh-value | rst rst-value | syn syn-value | urg urg-value } * | established } | counting | destination { dest dest-prefix | dest/dest-prefix | any } | destination-port operator port1 [ port2 ] | dscp dscp | flow-label flow-label-value | fragment | icmp6-type { icmp6-type icmp6-code | icmp6-message } | routing [ type routing-type ] | source { source source-prefix | source/source-prefix | any } | source-port operator port1 [ port2 ] | time-range time-range-name ] * View undo rule rule-id [ { { ack | fin | psh | rst | syn | urg } * | established } | counting | destination | destination-port | dscp | flow-label | fragment | icmp6-type | routing | source | source-port | time-range ] * IPv6 advanced ACL view Default level 2: System level Parameters rule-id: Specifies a rule ID, in the range of 0 to 65534. If no rule ID is provided when you create an ACL rule, the system automatically assigns it a rule ID. This rule ID takes the nearest higher multiple of the numbering step to the current highest rule ID, starting from 0. For example, if the rule numbering step is 5 and the current highest rule ID is 28, the rule is numbered 30. deny: Denies matching packets. permit: Allows matching packets to pass. 24