HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches ACL and QoS Command Refere - Page 31
Parameters, Function, Description, icmpv6, Table 11
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
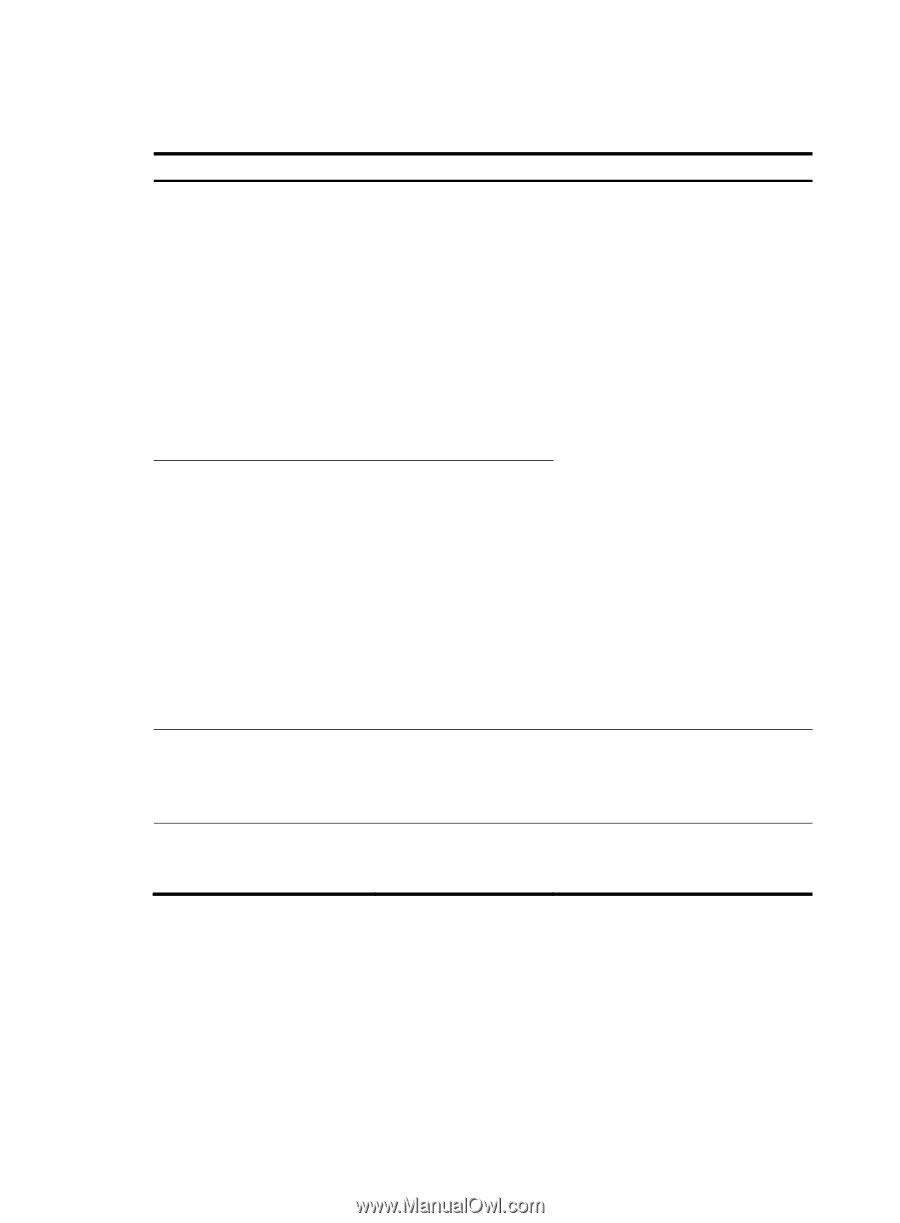
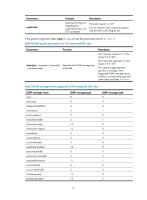
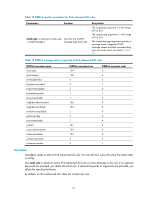
If the protocol argument takes tcp (6) or udp (17), you can set the parameters shown in Table 11. Table 11 TCP/UDP-specific parameters for IPv6 advanced ACL rules Parameters Function Description source-port operator port1 [ port2 ] Specifies one or more UDP or TCP source ports destination-port operator port1 [ port2 ] Specifies one or more UDP or TCP destination ports The operator argument can be lt (lower than), gt (greater than), eq (equal to), neq (not equal to), or range (inclusive range). The port1 and port2 arguments are TCP or UDP port numbers in the range of 0 to 65535. port2 is needed only when the operator argument is range. TCP port numbers can be represented in these words: chargen (19), bgp (179), cmd (514), daytime (13), discard (9), domain (53), echo (7), exec (512), finger (79), ftp (21), ftp-data (20), gopher (70), hostname (101), irc (194), klogin (543), kshell (544), login (513), lpd (515), nntp (119), pop2 (109), pop3 (110), smtp (25), sunrpc (111), tacacs (49), talk (517), telnet (23), time (37), uucp (540), whois (43), and www (80). UDP port numbers can be represented in these words: biff (512), bootpc (68), bootps (67), discard (9), dns (53), dnsix (90), echo (7), mobilip-ag (434), mobilip-mn (435), nameserver (42), netbios-dgm (138), netbios-ns (137), netbios-ssn (139), ntp (123), rip (520), snmp (161), snmptrap (162), sunrpc (111), syslog (514), tacacs-ds (65), talk (517), tftp (69), time (37), who (513), and xdmcp (177). { ack ack-value | fin fin-value | psh Specifies one or more TCP psh-value | rst rst-value | syn flags, including ACK, FIN, syn-value | urg urg-value } * PSH, RST, SYN, and URG Parameters specific to TCP. The value for each argument can be 0 (flag bit not set) or 1 (flag bit set). The TCP flags in one rule are ANDed. established Specifies the flags for indicating the established status of a TCP connection Parameter specific to TCP. The rule matches TCP connection packets with the ACK or RST flag bit set. If the protocol argument takes icmpv6 (58), you can set the parameters shown in Table 12. 26