HP ProLiant DL288 HP ProLiant DL288 G6 Server Software Configuration Guide - Page 14
Table 5, Field, Description, Options, Disabled L0s and L1.
 |
View all HP ProLiant DL288 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 14 highlights
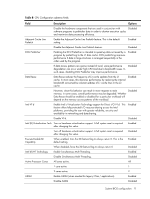
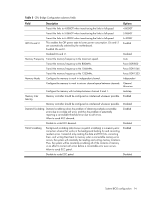
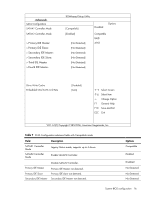
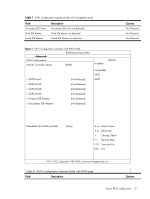
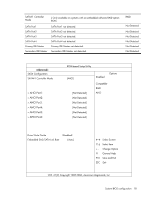
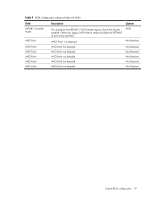
Table 5 CPU Bridge Configuration submenu fields Field Description Options Transit the links to 4.800GT when transitioning the links to full-speed. 4.800GT Transit the links to 5.866GT when transitioning the links to full-speed. 5.866GT QPI L0s and L1 Transit the links to 6.400GT when transitioning the links to full-speed. This enables the QPI power state to lower power consumption. L0s and L1 are automatically selected by the motherboard. Enabled L0s and L1. 6.400GT Enabled Disabled L0s and L1. Disabled Memory Frequency Transit the memory frequency to the maximum speed. Auto Transit the memory frequency to the 800MHz. Force DDR-800 Transit the memory frequency to the 1066MHz. Force DDR-1066 Transit the memory frequency to the 1333MHz. Force DDR-1333 Memory Mode Configure the memory to work in independent channel. Independent Configure the memory to work in mirrors channel space between channels. Channel Mirroring Configure the memory with Lockstep between channel 0 and 1. Lockstep Memory Inter leaving Memory controller should be configured as interleaved whenever possible. Enabled Memory controller should be configured as interleaved whenever possible. Disabled Demand Scrubbing Demand scrubbing solves the problem of obtaining multiple correctable errors due to a single soft error, and thus the problem of potentially reporting a correctable threshold error due to soft errors. Allow to scrub ECC demand. Enabled Disable to scrub ECC demand. Disabled Patrol Scrubbing Background scrubbing (also known as patrol scrubbing) is a memory errorcorrection scheme that works in the background looking for and correcting resident errors. Instead of only reading the data and ECC bits, correcting them, and writing them back to memory when a correctable memory error occurs, the system will constantly be reading and writing memory locations. Thus, the system will be constantly scrubbing all of the contents of memory in an effort to correct soft errors before a correctable error even occurs. Allow to scrub ECC patrol. Enabled Disable to scrub ECC patrol. Disabled System BIOS configuration 14