Intel Q9400S Data Sheet - Page 99
Boxed Intel, Core™2 Extreme Processor QX9650, Specifications
 |
UPC - 735858207973
View all Intel Q9400S manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 99 highlights
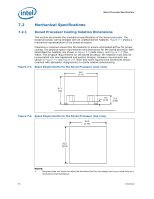
Boxed Processor Specifications 7.5 Note: If the boxed processor fan heatsink 4-pin connector is connected to a 4-pin motherboard header and the motherboard is designed with a fan speed controller with PWM output (CONTROL see Table 7-1) and remote thermal diode measurement capability the boxed processor will operate as follows: As processor power has increased the required thermal solutions have generated increasingly more noise. Intel has added an option to the boxed processor that allows system integrators to have a quieter system in the most common usage. The 4th wire PWM solution provides better control over chassis acoustics. This is achieved by more accurate measurement of processor die temperature through the processor's Digital Thermal Sensors (DTS) and PECI. Fan RPM is modulated through the use of an ASIC located on the motherboard that sends out a PWM control signal to the 4th pin of the connector labeled as CONTROL. The fan speed is based on actual processor temperature instead of internal ambient chassis temperatures. If the new 4-pin active fan heat sink solution is connected to an older 3-pin baseboard processor fan header it will default back to a thermistor controlled mode, allowing compatibility with existing 3-pin baseboard designs. Under thermistor controlled mode, the fan RPM is automatically varied based on the Tinlet temperature measured by a thermistor located at the fan inlet. For more details on specific motherboard requirements for 4-wire based fan speed control see the appropriate Thermal and Mechanical Design Guidelines (See Section 1.2). Boxed Intel® Core™2 Extreme Processor QX9650 Specifications This section documents the mechanical specifications of the Boxed Intel® Core™2 Extreme processor QX9650. The boxed processor will be shipped with an unattached fan heatsink. Figure 7-10 shows a mechanical representation of the boxed processor. Clearance is required around the fan heatsink to ensure unimpeded airflow for proper cooling. The physical space requirements and dimensions for the boxed processor with assembled fan heatsink are shown in Figure 7-3 (top view), and Figure 7-4 (side view). The airspace requirements for the boxed processor fan heatsink must also be incorporated into new baseboard and system designs. Airspace requirements are shown in Figure 7-11 and Figure 7-12. Note that some figures have centerlines shown (marked with alphabetic designations) to clarify relative dimensioning. The Boxed Intel® Core™2 Extreme processor QX9650 cooling solution violates the boxed processor keep out zones. This is done intentionally, and with the understanding that Extreme Edition systems will be integrated into larger capacity chassis. Datasheet 101