TP-Link TL-WA500G User Guide - Page 52
Appendix E: Glossary - specification
 |
UPC - 845973051105
View all TP-Link TL-WA500G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 52 highlights
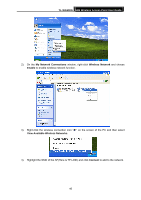
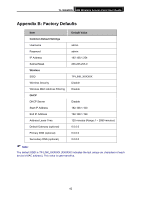
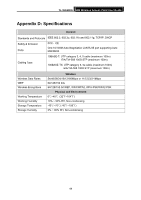
TL-WA500G 54M Wireless Access Point User Guide Appendix E: Glossary 2x to 3x eXtended RangeTM WLAN Transmission Technology - The WLAN device with 2x to 3x eXtended RangeTM WLAN transmission technology make its sensitivity up to 105 dBm, which gives users the ability to have robust, longer-range wireless connections. With this range-enhancing technology, a 2x to 3x eXtended RangeTM based client and access point can maintain a connection at as much as three times the transmission distance of traditional 802.11b and 802.11g products, for a coverage area that is up to nine times greater. A traditional 802.11b and 802.11g product transmission distance is about 300m. A 2x to 3x eXtended RangeTM based client and access point can maintain a connection transmission distance may be up to 830m. 802.11b - The 802.11b standard specifies a wireless networking at 11 Mbps using direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) technology and operating in the unlicensed radio spectrum at 2.4GHz, and WEP encryption for security. 802.11b networks are also referred to as Wi-Fi networks. 802.11g - specification for wireless networking at 54 Mbps using direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) technology, using OFDM modulation and operating in the unlicensed radio spectrum at 2.4GHz, and backward compatibility with IEEE 802.11b devices, and WEP encryption for security. Access Point (AP) - A wireless LAN transceiver or "base station" that can connect a wired LAN to one or many wireless devices. Access points can also bridge to each other. DNS (Domain Name System) - An Internet Service that translates the names of websites into IP addresses. Domain Name - A descriptive name for an address or group of addresses on the Internet. DoS (Denial of Service) - A hacker attack designed to prevent your computer or network from operating or communicating. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) - A technology that allows data to be sent or received over existing traditional phone lines. ISP (Internet Service Provider) - A company that provides access to the Internet. MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) - The size in bytes of the largest packet that can be transmitted. SSID - A Service Set Identification is a thirty-two character (maximum) alphanumeric key identifying a wireless local area network. For the wireless devices in a network to communicate with each other, all devices must be configured with the same SSID. This is typically the configuration parameter for a wireless PC card. It corresponds to the ESSID in the wireless Access Point and to the wireless network name. WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) - A data privacy mechanism based on a 64-bit or 128-bit or 152-bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard. Wi-Fi - A trade name for the 802.11b wireless networking standard, given by the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA, see http://www.wi-fi.net), an industry standards group promoting interoperability among 802.11b devices. WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) - A group of computers and associated devices communicate with each other wirelessly, which network serving users are limited in a local area. 45