ZyXEL NWA1123-NI User Guide - Page 58
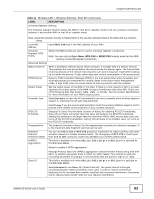
User Authentication, None., WPA2., WPA2-MIX., WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK-MIX
 |
View all ZyXEL NWA1123-NI manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 58 highlights
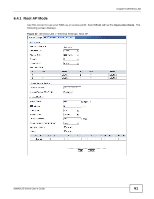
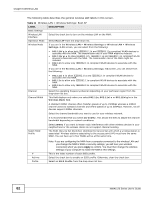
Chapter 6 Wireless LAN The NWA secure communications via data encryption, wireless client authentication and MAC address filtering. It can also hide its identity in the network. User Authentication Authentication is the process of verifying whether a wireless device is allowed to use the wireless network. You can make every user log in to the wireless network before they can use it. However, every device in the wireless network has to support IEEE 802.1x to do this. For wireless networks, you can store the user names and passwords for each user in a RADIUS server. This is a server used in businesses more than in homes. If you do not have a RADIUS server, you cannot set up user names and passwords for your users. Unauthorized wireless devices can still see the information that is sent in the wireless network, even if they cannot use the wireless network. Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized wireless users to get a valid user name and password. Then, they can use that user name and password to use the wireless network. The following table shows the relative effectiveness of wireless security methods:. Table 10 Wireless Security Levels SECURITY LEVEL SECURITY TYPE Least Secure Unique SSID (Default) Unique SSID with Hide SSID Enabled MAC Address Filtering WEP Encryption IEEE802.1x EAP with RADIUS Server Authentication Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Most Secure WPA2 The available security modes in your NWA are as follows: • None. No data encryption. • WEP. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption scrambles the data transmitted between the wireless stations and the access points to keep network communications private. • WPA. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard. • WPA2. WPA2 (IEEE 802.11i) is a wireless security standard that defines stronger encryption, authentication and key management than WPA. • WPA2-MIX. This commands the NWA to use either WPA2 or WPA depending on which security mode the wireless client uses. • WPA-PSK. This adds a pre-shared key on top of WPA standard. • WPA2-PSK. This adds a pre-shared key on top of WPA2 standard. • WPA2-PSK-MIX. This commands the NWA to use either WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK depending on which security mode the wireless client uses. Note: To guarantee 802.11n wireless speed, please only use WPA2 or WPA2-PSK security mode. Other security modes may degrate the wireless speed performance to 802.11g. 58 NWA1120 Series User's Guide