D-Link DES-1210-52 Product Manual - Page 55
Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings, From Port/To Port, State, External Cost
 |
UPC - 790069327827
View all D-Link DES-1210-52 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 55 highlights
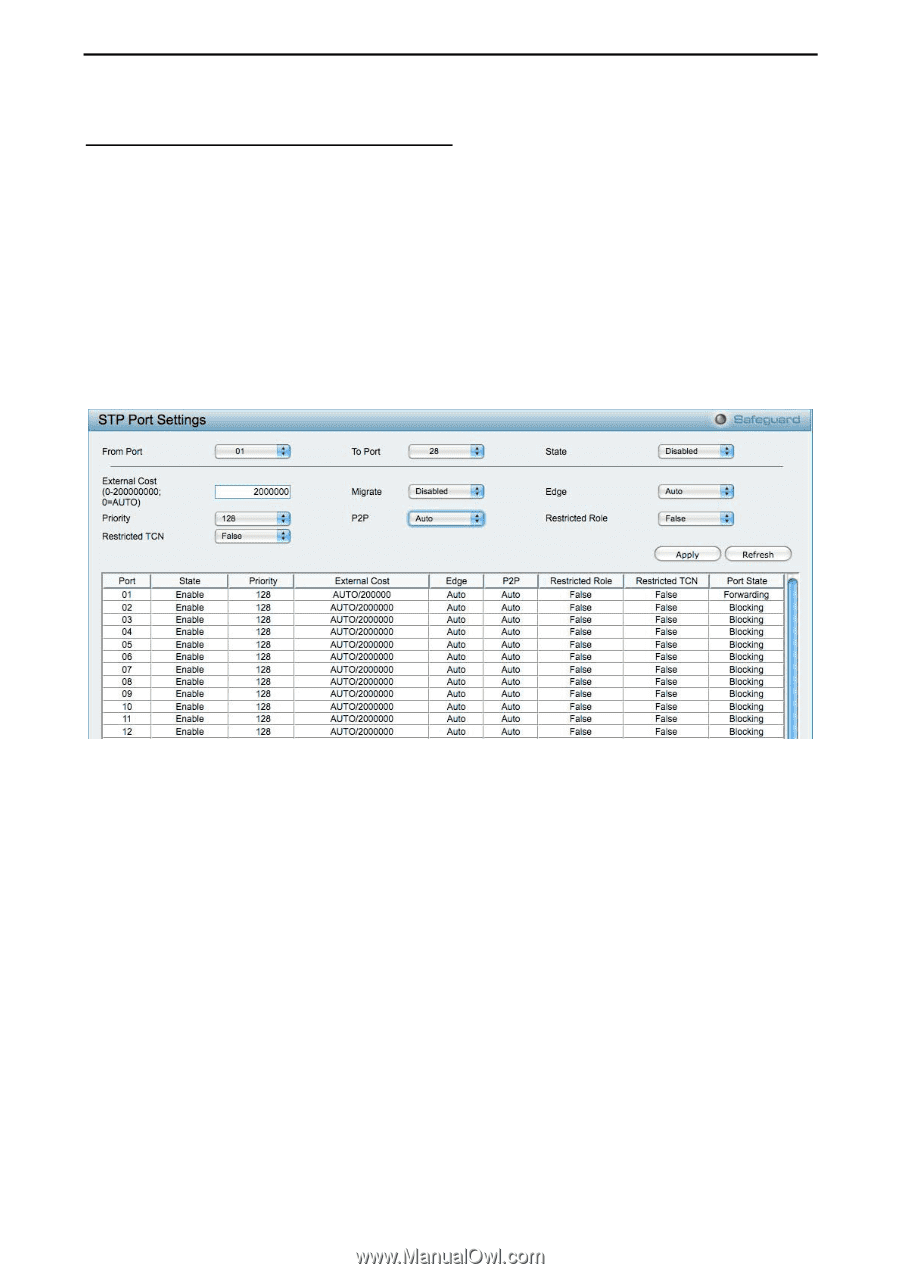
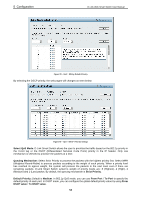
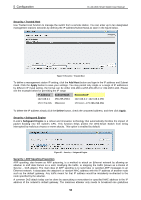
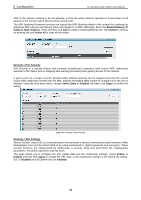
5 Configuration D-Link Web Smart Switch User Manual Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings STP can be set up on a port per port basis. In addition to setting Spanning Tree parameters for use on the switch level, the Switch allows for the configuration of groups of ports, each port-group of which will have its own spanning tree, and will require some of its own configuration settings. An STP Group spanning tree works in the same way as the switch-level spanning tree, but the root bridge concept is replaced with a root port concept. A root port is a port of the group that is elected based on port priority and port cost, to be the connection to the network for the group. Redundant links will be blocked, just as redundant links are blocked on the switch level. The STP on the switch level blocks redundant links between switches (and similar network devices). The port level STP will block redundant links within an STP Group. It is advisable to define an STP Group to correspond to a VLAN group of ports. Figure 86 - Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings From Port/To Port: A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port. State: Use the drop-down menu to enable or disable STP by per-port based. It will be selectable after the global STP is enabled. External Cost: This defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding packets to the specified port list. Port cost can be set automatically or as a metric value. The default value is 0 (auto). 0 (auto) - Setting 0 for the external cost will automatically set the speed for forwarding packets to the specified port(s) in the list for optimal efficiency. Default port cost: 100Mbps port = 200000. Gigabit port = 20000. Value 1-200000000 - Define a value between 1 and 200000000 to determine the external cost. The lower the number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen to forward packets. Migrate: Setting this parameter as Yes will set the ports to send out BPDU packets to other bridges, requesting information on their STP setting. If the Switch is configured for RSTP, the port will be capable to migrate from 802.1d STP to 802.1w RSTP. Migration should be set as yes on ports connected to network stations or segments that are capable of being upgraded to 802.1w RSTP on all or some portion of the segment. 49