D-Link DSN-540 CLI User's Guide for DSN-1100-10 - Page 26
Isa_hostname, Admin, Isa_username, Isa_password
 |
UPC - 790069324017
View all D-Link DSN-540 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
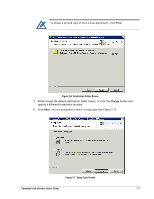
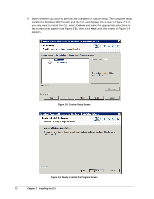
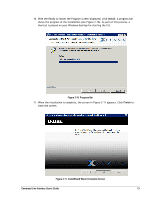
Page 26 highlights
3. Optional: To add an IP address of the array management port, username, and password, or script file name after the CLI executable name, or to disable any real-time indications, type the option (which consists of a switch and an entry such as an IP address or hostname) after the name of the CLI executable, as shown in the following steps. Separate the CLI executable filename from these options with a space. Adding a system IP address or host name: -g See the example in Figure 2-13. If -g is omitted, the environment variable ISA_HOSTNAME is used. If that environment variable is not defined, you are prompted for an IP address if none is found. Adding a username: -u Adding a password: -p The default username and password are admin (see the example in Figure 2-13). If -u is omitted, the environment variable ISA_USERNAME is used. If -p is omitted, the ISA_PASSWORD environment variable is used. If these environment variables are not defined, you are prompted for a username and/or password if none is found. Figure 2-13. Example of Using the -g, -u, and -p Switches Running a script: -x See the examples in Figure 2-14 and Figure 2-15. The name of the script file referenced in the Open field should have the file name scriptFileName.cli. The file name entered in the Open field should not include the .cli extension. In Figure 2-14, for instance, the command line will have the CLI run a script called createJbodScript, which creates a JBOD on the array. The 10GB following the script name tells the CLI to create a 10 GB volume called myVolName on that JBOD. In Figure 2-15, the command line will provide the IP address, username, and password for logging in and run the same script as in Figure 2-14, without creating the 10 GB volume. Figure 2-14. Example of Using the -x Switch 16 Chapter 2 Installing the CLI