D-Link G604T Product Manual - Page 46
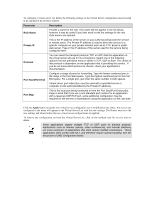
Parameter, Description, Rule Name, Private IP, Protocol, Port Start/Port End, Port Map - port forwarding
 |
UPC - 790069265662
View all D-Link G604T manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 46 highlights
To configure a virtual server set, define the following settings in the Virtual Server configuration menu located in the top half of the browser window. Parameter Description Rule Name Provide a name for the rule. This name will not appear in the list below, however it may be useful if you later need to edit the settings for the rule. Rule names are optional. Private IP This is the IP address of the server on your LAN that will provide the service to remote users. The Private IP address is used to direct the service to a specific computer on your private network such as an FTP, Email or public web server. Type in the IP address of the server used for the service being configured here. Protocol You can select the transport protocol (TCP or UDP) that the application on the virtual server will use for its connections. Select one of the following options from the pull-down menu to define a TCP, UDP or Both. The choice of this protocol is dependent on the application that is providing the service. If you do not know which protocol to choose, check your application's documentation. Port Start/Port End Configure a range of ports for forwarding. Type the lowest numbered port in the range in the Port Start space. Type the highest numbered port in the Port End space. For a single port, just enter the same number in both spaces. Virtual server port redirection must be used with a specified server or computer on the LAN (identified by the Private IP address). Port Map This is the local port being forwarded to from the Port Start/Port End port(s). Keep in mind that if you use a non-standard port number for an application with a reserved UDP/TCP port, some additional configuration may be required for the servers or workstations using the application on the LAN side. Click the Apply button to put the new virtual server configuration set or modification into effect. Any server sets configured in the menu will appear in the Virtual Server List with the new settings. The Router must save the new settings and reboot before the new virtual server configurations are applied. To remove any configuration set from the Virtual Server List, click on the trashcan icon for set you want to delete. Note Some applications require multiple TCP or UDP ports to function properly. Applications such as Internet gaming, video conferencing, and Internet telephony are some examples of applications that often require multiple connections. These applications often conflict with NAT, and therefore require special handling. See the discussion of DMZ configuration below.