Intel SE7505VB2 Product Specification - Page 24
AGP 8X Bus, P64H2, PCI Bus P64-B I/O Subsystem, ICH4
 |
View all Intel SE7505VB2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 24 highlights
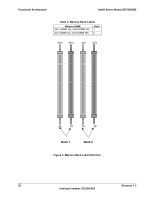
Functional Architecture Intel® Server Board SE7505VB2 3.2.2.1 AGP 8X Bus The AGP 8X bus features include the following: Single AGP device AGP interface asynchronously coupled to core AGP 3.0 specification compliant AGP 8X / 4X / 2X at 1.5V 0.8V and 1.5V AGP electrical. No 3.3V support Isochronous support for AGP 8X, non-snooped 32 deep AGP request queue 32-bit upstream address support for inbound AGP and PCI cycles 32-bit downstream address support for outbound PCI and fast write cycles 3.2.3 P64H2 The P64H2 is a 567-ball FC-BGA device that provides an integrated I/O bridge for a highperformance data flow path between the HI 2.0 bus and the 64-bit I/O subsystem. This subsystem supports peer 64-bit PCI-X segments. Because it has two PCI interfaces, the P64H2 can provide large and efficient I/O configurations. The P64H2 functions as the bridge between the HI 2.0 interface and the two 64-bit PCI-X I/O segments. The HI interface can support 1GB/s of data bandwidth. 3.2.3.1 PCI Bus P64-B I/O Subsystem P64-B supports two 184-pin, 3.3-volt keyed, 64-bit PCI expansion slot connectors running at 100MHz. Both of the slots support 184-pin, 3.3V keyed, 64-bit PCI-X expansion cards. Both slots support full-length PCI-X or PCI add-in cards. The BIOS is responsible for setting the bus speed of P64-B. The bus speed runs at the speed of the slowest card installed. 3.2.3.2 PCI Bus P64-C I/O Subsystem P64-C supports the following embedded devices and connectors: One 184-pin, 3.3-volt keyed, 64-bit PCI expansion slot connector running at 66MHz. This slot is capable of supporting a full-length add-in PCI card One integrated Intel® 82540EM fast Ethernet gigabit (10/100/1000) controller The BIOS is responsible for setting the bus speed of P64-C. The bus speed runs at the speed of the slowest card installed. 3.2.4 ICH4 The ICH4 is a multi-function device, housed in a 421-pin BGA device, providing a HI 1.5 to PCI bridge, a PCI IDE interface, a PCI USB controller, and a power management controller. Each function within the ICH4 has its own set of configuration registers. Once configured, each appears to the system as a distinct hardware controller sharing the same PCI bus interface. 24 Revision 1.2 Intel part number C32194-002