Netgear WN604 User Manual - Page 29
Con WEP, Configuration > Security - password
 |
UPC - 606449070712
View all Netgear WN604 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 29 highlights
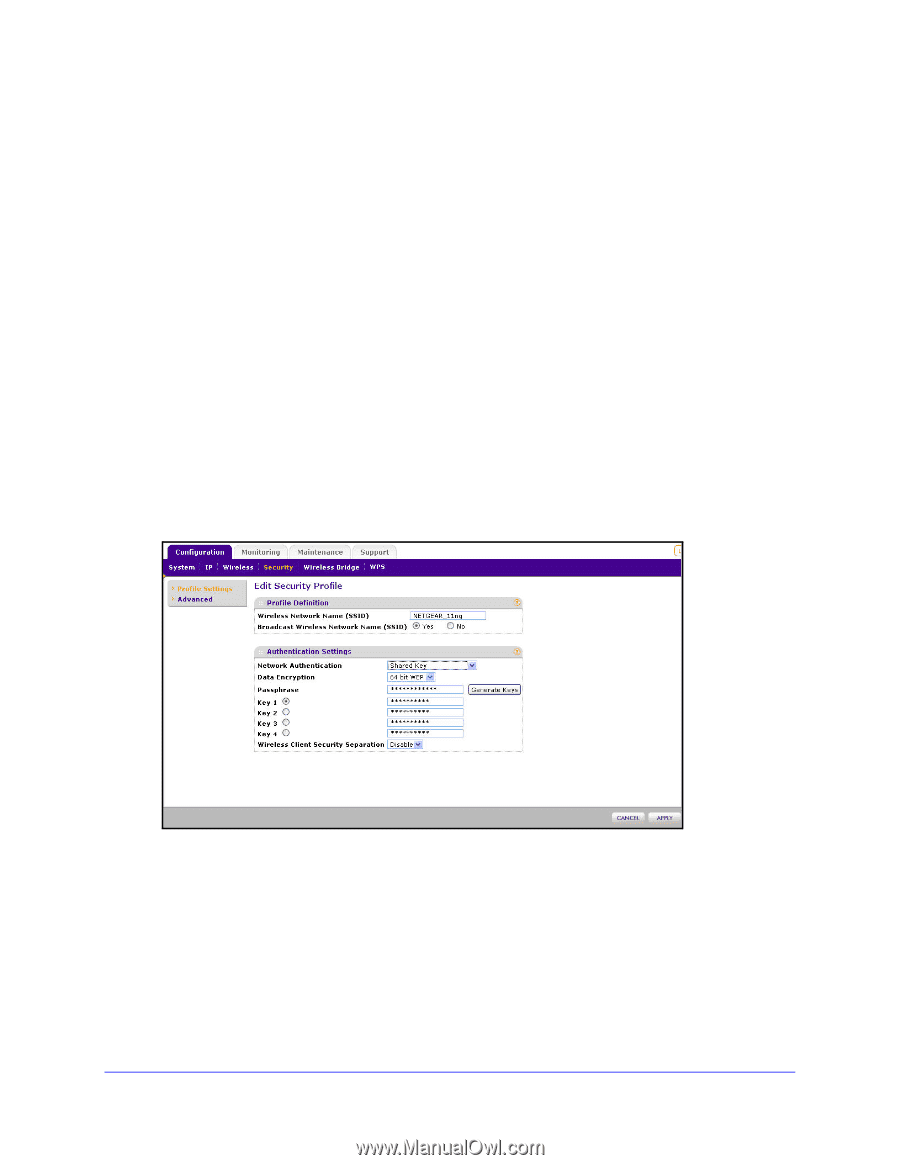
Wireless N150 Access Point WN604 • WPA2-PSK. With this setting, only wireless clients that support WPA2 can access the wireless network. By default, the Data Encryption field is set to AES. • WPA-PSK & WPA2-PSK. Wireless clients using WPA2 or WPA can access the wireless network. By default, the Data Encryption field is set to TKIP+AES. • WPA-TKIP. Wireless clients using WPA can access the wireless network. 3. In the WPA Passphrase (Network Key) field, enter the password that you want to use to secure the wireless network. 4. Wireless client security separation is disabled by default. If it is enabled, associated wireless clients cannot communicate with each other. (This feature is intended for hotspots and other public access situations.) 5. Click Apply to save your settings. Configure WEP WEP is a legacy security option. NETGEAR recommends that you use WPA2 or WPA. To configure WEP data encryption: 1. Select Configuration > Security. The Edit Security Profile screen displays. 2. From the Network Authentication drop-down list, select either Open System or Shared Key authentication. 3. From the Data Encryption drop-down list, select encryption strength (64 bits, 128 bits, or 152 bits). 4. You manually or automatically program the four data encryption keys. These values have to be identical on all PCs and access points in your network. Select one of the following: • Automatic. Enter a word or group of printable characters in the Passphrase field and click the Generate Keys button. The four key fields are automatically populated with key values. • Manual. Enter the number of hexadecimal digits appropriate to the encryption strength: 10 digits for 64-bit, 26 digits for 128-bit, and 32 digits for 152-bit (any combination of 0-9, a-f, or A-F). Configure Security 29