Symantec 10099585 User Guide - Page 80
FTP File Transfer, hidden attribute
 |
UPC - 037648232289
View all Symantec 10099585 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 80 highlights
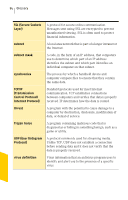
80 Glossary extension FAT (file allocation table) file type Finder firewall rule fragmented fragmented IP packet FTP (File Transfer Protocol) hidden attribute host name The three-letter ending on a file name that associates the file with an activity or program. Examples include .txt (text) and .exe (executable program). A system table (used primarily by DOS and Windows 9x/Me) that organizes the exact location of the files on the hard drive. A code that associates the file with a program or activity, often appearing as the file name extension, such as .txt or .jpeg. The program that manages your Macintosh disk and file activity and display. Parameters that define how a firewall reacts to specific data or network communications. A firewall rule usually contains a data pattern and an action to take if the pattern is found. When the data that makes up a file is stored in noncontiguous clusters across a disk. A fragmented file takes longer to read from the disk than an unfragmented file. An IP packet that has been split into parts. Packets are fragmented if they exceed a network's maximum packet size, but malicious users also fragment them to hide Internet attacks. An application protocol used for transferring files between computers over TCP/IP networks such as the Internet. A file attribute that makes files harder to access and more difficult to delete than other files. It also prevents them from appearing in a DOS or Windows directory list. The name by which most users refer to a Web site. For example, www.symantec.com is the host name for the Symantec Web site. Host names are translated to IP addresses by the DNS.