TP-Link T1700X-16TS T1700X-16TSUN V1 User Guide - Page 106
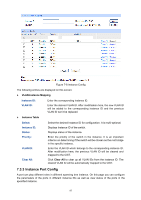
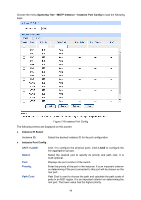
UNIT:1/LAGS, Select, Status, Priority, ExtPath Cost, IntPath Cost, Edge Port, P2P Link, MCheck, Port
 |
View all TP-Link T1700X-16TS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 106 highlights
The following entries are displayed on this screen: Port Config UNIT:1/LAGS: Click 1 to configure the physical ports. Click LAGS to configure the link aggregation groups. Select: Port: Status: Priority: Select the desired port for STP configuration. It is multi-optional. Displays the port number of the switch. Enable /Disable STP function for the desired port. Enter a value from 0 to 240 divisible by 16. Port priority is an important criterion on determining if the port connected to this port will be chosen as the root port. The lower value has the higher priority. ExtPath Cost: ExtPath Cost is used to choose the path and calculate the path costs of ports in different MST regions. It is an important criterion on determining the root port. The lower value has the higher priority. IntPath Cost: IntPath Cost is used to choose the path and calculate the path costs of ports in an MST region. It is an important criterion on determining the root port. The lower value has the higher priority. Edge Port: Enable/Disable Edge Port. The edge port can transit its state from blocking to forwarding rapidly without waiting for forward delay. P2P Link: Select the P2P link status. If the two ports in the P2P link are root port or designated port, they can transit their states to forwarding rapidly to reduce the unnecessary forward delay. MCheck: Enable to perform MCheck operation on the port. Unchange means no MCheck operation. Port Mode: Port Role: Port Status: Display the spanning tree mode of the port. Displays the role of the port played in the STP Instance. Root Port: Indicates the port that has the lowest path cost from this bridge to the Root Bridge and forwards packets to the root. Designated Port: Indicates the port that forwards packets to a downstream network segment or switch. Master Port: Indicates the port that connects a MST region to the common root. The path from the master port to the common root is the shortest path between this MST region and the common root. Alternate Port: Indicates the port that can be a backup port of a root or master port. Backup Port: Indicates the port that is the backup port of a designated port. Disabled: Indicates the port that is not participating in the STP. Displays the working status of the port. Forwarding: In this status the port can receive/forward data, receive/send BPDU packets as well as learn MAC address. Learning: In this status the port can receive/send BPDU packets and learn MAC address. Blocking: In this status the port can only receive BPDU packets. Disconnected: In this status the port is not participating in the STP. 95