ZyXEL N220 User Guide - Page 49
Station Mode, 4.1 Overview, 4.1.1 What You Can Do in This What You Need to Know
 |
View all ZyXEL N220 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
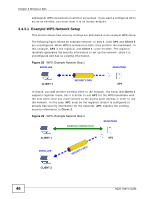
CHAPTER 4 Station Mode 4.1 Overview This section shows you how to configure your N220 using the ZyXEL utility in Windows. Note: Some features available in Windows XP or Windows 2000 are not available in Windows Vista. 4.1.1 What You Can Do in This Section • On the Link Info screen, you can see your current connection details, monitor signal strength and quality, and more. See Section 4.3 on page 51 for details. • On the Site Survey screen, you can connect to any available unsecured wireless network in range of the N220, or open the security settings screen for any secured wireless network in range. See Section 4.4 on page 54 for details. • On the Profile screen, you can create, delete and manage your wireless network profiles. See Section 4.5 on page 62 for details. • On the Adapter screen, you can configure the N220 hardware, such as activating WPS mode or its power saving feature. See Section 4.6 on page 68 for details. 4.1.2 What You Need to Know The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this section. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encrypts data transmitted between wired and wireless networks to keep the transmission private. Although one of the original wireless encryption protocols, WEP is also the weakest. Many people use it strictly to deter unintentional usage of their wireless network by outsiders. Wi-fi Protected Access (WPA) Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i standard. It improves data encryption by using Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP), N220 User's Guide 49