Compaq ProLiant 1000 PCI Bus Numbering in a Microsoft Windows NT Environment - Page 11
Configuration Changes, Windows NT and PCI Bus Numbering, PCI Bus Numbering and Network Controllers
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
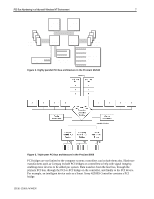
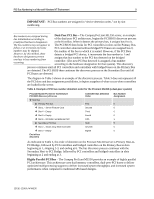
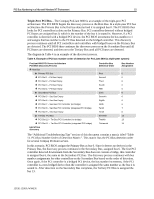
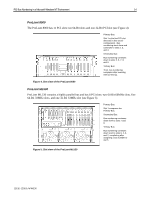
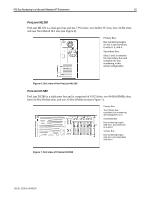
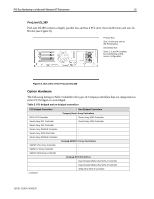
PCI Bus Numbering in a Microsoft Windows NT Environment 11 For example, the order of detection on the ProLiant 8000 is Primary Host-to-PCI Bridge, followed by PCI controllers and bridged controllers on the Primary Bus in slots beginning at 1, 2, 3 and ending at slot 4. The bus discovery process continues with the Secondary Host-to-PCI Bridge, followed by PCI controllers and bridged controllers in slots beginning at 5, 6, 7, 8, and ending at slot 9. Then, the process moves forward to the Tertiary Host-to-PCI Bridge, followed by PCI controllers and bridges controllers in slots beginning at 10 and ending at slot 11. Configuration Changes Bus number assignments for controllers with bridged devices are assigned to the PCI bus on the From time to time, network administrators add disk and network controllers to existing configurations to address the requirements of growing server networks. Adding a bridged controller earlier in the controller. discovery order than other existing controllers can change the PCI bus number assignment of all bridged PCI controllers detected after it. Each subsequent controller in the discovery process (containing a bridged PCI bus) receives an incremented bus number assignment, regardless of whether it is new or it was previously configured. The PCI BIOS assigns resources at power-up, the server must be restarted before the PCI BIOS can assign PCI bus numbers to each bus discovered in the new configuration. The PCI BIOS assigns PCI bus numbers to each PCI device in the order of discovery without any concern for prior bus assignments or the physical slot location. Several bus-numbering scenarios included in this white paper demonstrate how the PCI BIOS discovers PCI buses and assigns numbers. Windows NT and PCI Bus Numbering During the initial installation of Windows NT, all network controllers in the server automatically add to the registry along with the bus number assignment. This is the only time that Windows NT automatically adds the PCI bus numbers in the registry. If no physical configuration changes are made to the system in the future, Windows NT continues to detect the controllers after future system restarts. IMPORTANT: During the development of Microsoft Windows 2000, Compaq and Microsoft worked closely together effectively implementing Windows 2000 on Compaq hardware. Through this partnership, device detection improved, eliminating PCI bus numbering issues in the Windows 2000 environment. Windows 2000 checks and resets registry settings automatically, unlike its predecessor that does not reset the registry settings after discovering unbound devices. PCI Bus Numbering and Network Controllers When you modify a server by adding a new controller, removing a controller, or moving a controller to a different slot, Windows NT might not detect the change in the server configuration. Configuration changes only occur when you insert or remove a bridged device. The PCI BIOS renumbers PCI bus numbers assigned to PCI buses and PCI bridged devices during the discovery process, based on the new configuration. Windows NT does not automatically check for new bus number assignments. Windows NT retains the original controller slot number and bus number assignments in its registry after the server restarts. However, the bus number assignments in the Windows NT registry can be updated using the appropriate network configuration tool for your controllers. The Compaq TLAN Teaming and Configuration Utility supports Compaq NetFlex-3 and Netelligent Controllers (see Appendix C for usage information), 13UK-1200A-WWEN