Compaq ProLiant 1000 PCI Bus Numbering in a Microsoft Windows NT Environment - Page 3
Executive Overview, How Windows NT handles bus numbering in the Windows NT Registry. - proliant 8000
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 3 highlights
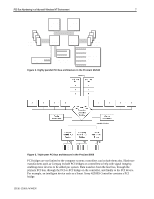
PCI Bus Numbering in a Microsoft Windows NT Environment 3 Executive Overview The term Peripheral Component Interconnect, commonly known as PCI, refers to the bus architecture standard. The PCI bus technology has become an industry standard; today's servers provide a large number of expansion slots and can be populated with a greater number of PCI disk and network controllers. PCI buses provide fast access between controllers and/or system memory and the host processor. PCI buses offer a significant performance advantage over EISA buses. The PCI Special Interest Group (SIG) is an unincorporated association of members of the microcomputer industry set up for the purpose of monitoring and enhancing the development of the PCI architecture. The PCI Steering Committee is a group of nine companies that oversees SIG activities and reviews formal recommendations for changes to PCI Specification(s). Compaq is a member of the SIG Steering Committee and actively proposes and contributes new design functions for future revisions to the PCI Specification. Later in this document, examples are provided in two test scenarios, illustrating what happens to PCI PCI bus technology development continues to advance at a rapid pace to meet customer's business requirements. Server technology includes equipment, such as the ProLiant 8000 with multiple PCI buses. The bus numbering when configuration computing capabilities of these servers can be further expanded through changes occur. PCI controllers and PCI bridged devices such as the Smart Array 4250ES Controller. Each PCI bus in the system is numbered by the PCI BIOS during system start up. Windows NT uses these numbers to identify bridged controllers. If controllers are added to an existing system, the PCI bus numbering might change. This change might affect the operation of your system. This white paper provides information to help systems professionals understand how the PCI Specification addresses server bus numbering assignments. This document discusses: • How the PCI BIOS detects and numbers PCI buses and bridges. • What happens to PCI Bus numbering at each system start up. • How adding or removing PCI devices might cause a renumbering of PCI buses. • How Windows NT handles bus numbering in the Windows NT Registry. • How to prevent PCI bus numbering mismatches from occurring. This document contains several examples to demonstrate PCI bus numbering. After reading this document, you should be able to properly configure and/or reconfigure a Windows NT system when PCI bus numbers are reassigned with minimal interruption to the network. 13UK-1200A-WWEN