Compaq ProLiant 1000 PCI Bus Numbering in a Microsoft Windows NT Environment - Page 4
PCI Bus Architecture Terminology, PCI System Architecture, Third Edition, MindShare
 |
View all Compaq ProLiant 1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 4 highlights
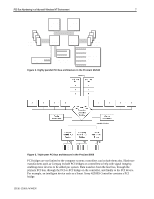
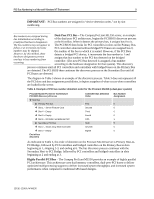
PCI Bus Numbering in a Microsoft Windows NT Environment 4 PCI Bus Architecture Terminology Table 1 lists some terms related to PCI Bus Architecture terminology. Some of the terminology defined in this table was referenced from PCI System Architecture, Third Edition, MindShare, Inc. Tom Shanley and Don Anderson. (November, 1995.) Table 1. PCI bus architecture standard terms Bridge Bus Number Device ID Downstream Dual-Peer PCI Bus Highly Parallel Architecture PCI PCI BIOS PCI Bridge PCI-to-PCI Bridge Bridge is the device, providing connectivity between two independent buses. Bus number is a number in the range 0...255 that uniquely selects a PCI bus. Device ID is a number in the range 0...31 that uniquely selects a device on a PCI bus. When a transaction is initiated and is passed through one or more PCI-toPCI bridges flowing away from the host processor, it is said to be moving downstream. A system architecture providing high-bandwidth I/0 because two buses can operate simultaneously (i.e., in parallel) is called a dual-peer-PCI bus. A system architecture using dual memory controllers, dual-peer-PCI buses to deliver optimized multiprocessing support to deliver increased system throughput and increased system performance when compared to traditional x86-based designs is said to be highly parallel. Peripheral Component Interconnect refers to a bus based on the PCI Local Bus Specification, through which industry-standard peripheral controllers connect to computer systems. PCI BIOS functions provides a software interface to the hardware used to implement a PCI based system. The device that provides the bridge between two independent buses. PCI bridges can reside on the system and can reside on controllers. PCI bridges help with signal integrity and allow more devices to be added per system. PCI-to-PCI bridge is a system architecture where an additional PCI bus is bridged off another PCI bus (i.e., in series). Peer-to-Peer PCI Buses Primary Bus Secondary Bus Tertiary Bus Triple-Peer PCI Bus PCI buses that occupy the same ranking in the PCI bus hierarchy (with respect to the host bus) are referred to as Peer PCI buses. The PCI bus closest to the host processor that is connected to one side of the inter-bus bridge is the Primary Bus (numbering always starts at 0). The PCI bus detected after the Primary Bus is called the Secondary Bus. The Tertiary bus resides furthest from host processor that is connected to one side of the inter-bus bridge. System architecture operating with three PCI buses on a single server is referred to as a Triple-Peer PCI Bus. Upstream When a transaction is initiated and is passed through one or more PCI-toPCI bridges flowing towards the host processor, it is said to be moving upstream. 13UK-1200A-WWEN