D-Link DES 6000 Product Manual - Page 86
IP Address, Switch Module, Apply, Switch MAC Address, Get IP from, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway
 |
UPC - 790069239328
View all D-Link DES 6000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 86 highlights
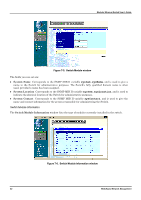
Modular Ethernet Switch User's Guide IP Address Figure 7-4. IP Address window You can change the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway on the Switch. If your are not using BOOTP, enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway of the Switch. If you enable BOOTP Service, you do not need to configure any IP parameters because a BOOTP server automatically assigns IP configuration parameters to the Switch. Click Apply to activate the new settings. The information above is described as follows: ♦ Switch MAC Address The Ethernet address for the switch. Also known as the physical address. ♦ Get IP from Choose either Manual, where you assign them in the fields below, BOOTP or DHCP. The BootP and DHCP protocols allow IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways to be assigned on a central server. If this option is enabled, when the Switch is first powered up it will look for the appropriate server to provide it with these settings. ♦ IP Address The IP Address for the switch on the TCP/IP network. ♦ Subnet Mask The subnet mask that controls subnetting on your TCP/IP network. ♦ Default Gateway The IP address of the device, usually a router, that handles connections to other subnets and/or other TCP/IP networks. Switch Module The Switch Module screen shows various pieces of information about your Switch, and allows you to set the System Name, System Location, and System Contact. Web-Based Network Management 81