D-Link DES 6000 Product Manual - Page 93
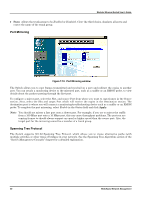
Forwarding and Filtering, STP Port Settings window
 |
UPC - 790069239328
View all D-Link DES 6000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 93 highlights
STP Port Settings Modular Ethernet Switch User's Guide Figure 7-12. STP Port Settings window Enter the desired Spanning Tree custom settings on this screen and then click Apply. The information above is described as follows: ♦ STP Status The Spanning Tree Protocol state for a selected port can either be Enabled or Disabled. ♦ Cost The Path Cost is a read-only parameter which is the first consideration when deciding on a designated port for switch to switch connections. Each 10Mbps port has a predefined cost of 100. Each 100Mbps port has an assigned Path Cost of 19. Gigabit ports have a cost of 4. Trunked ports have a cost of (base cost) minus (no. of ports in the group). ♦ Priority Port Priority is a read-write object that can be set from 0 to 255. The priority is used to determine the designated port if the Path costs of redundant switch to switch connections are the same. The higher the port priority, the more chance the port has of becoming the designated port. Zero is the highest priority. Forwarding and Filtering When a packet hits the Switch, it looks in the filtering and forwarding tables to decide what to do with the packet; either to filter it off the network, or to forward it through the port on which its destination lies. 88 Web-Based Network Management