D-Link DES 6000 Product Manual - Page 91
Port Mirroring, Spanning Tree Protocol, State, Apply
 |
UPC - 790069239328
View all D-Link DES 6000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 91 highlights
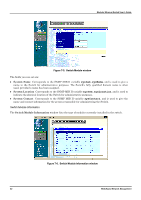
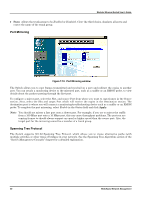
Modular Ethernet Switch User's Guide ♦ State Allows the trunk group to be Enabled or Disabled. Clear the third choice, deselects all ports and erases the name of the trunk group. Port Mirroring Figure 7-10. Port Mirroring window The Switch allows you to copy frames transmitted and received on a port and redirect the copies to another port. You can attach a monitoring device to the mirrored port, such as a sniffer or an RMON probe, to view details about the packets passing through the first port. To configure a mirror port, select the Slot, and source Port from where you want to copy frames in the Source section. Next, select the Slot and target Port which will receive the copies in the Destination section. The destination port is where you will connect a monitoring/troubleshooting device such as a sniffer or an RMON probe. To complete the port mirroring, select Enable in the Status field and click Apply. Note: You should not mirror a fast port onto a slower port. For example, if you try to mirror the traffic from a 100 Mbps port onto a 10 Mbps port, this can cause throughput problems. The port you are copying frames to should always support an equal or higher speed than the source port. Also, the target port for the mirroring cannot be a member of a trunk group. Spanning Tree Protocol The Switch supports 801.2d Spanning Tree Protocol, which allows you to create alternative paths (with multiple switches or other types of bridges) in your network. See the Spanning Tree Algorithm section of the "Switch Management Concepts" chapter for a detailed explanation. 86 Web-Based Network Management