D-Link DWS-3250 Product Manual - Page 331
TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol, Simple Network Time Protocol, Transport Control Protocol
 |
UPC - 790069289996
View all D-Link DWS-3250 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 331 highlights
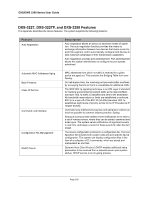
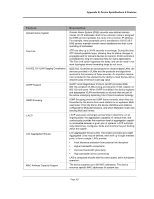
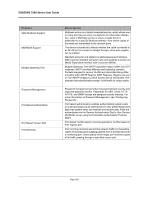
DXS/DWS 3200 Series User Guide Feature SNTP Spanning Tree Protocol SSH 2.0 SSL 3.0 Static MAC Entries TACACS+ TCP TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol Traceroute Virtual Cable Testing Description The Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) assures accurate network Ethernet Switch clock time synchronization up to the millisecond. Time synchronization is performed by a network SNTP server. Time sources are established by Stratums. Stratums define the distance from the reference clock. The higher the stratum (where zero is the highest), the more accurate the clock. 802.1d Spanning tree is a standard Layer 2 switch requirement that allows bridges to automatically prevent and resolve L2 forwarding loops. Switches exchange configuration messages using specifically formatted frames and selectively enable and disable forwarding on ports. Secure Shell (SSH) is a protocol that provides a secure, remote connection to a device. SSH version 2 is currently supported. The SSH server feature enables an SSH client to establish a secure, encrypted connection with a device. This connection provides functionality that is similar to an inbound telnet connection. SSH uses RSA and DSA Public Key cryptography for device connections and authentication. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is an application-level protocol that enables secure transactions of data through privacy, authentication, and data integrity. It relies upon certificates and public and private keys. MAC entries can be manually entered in the Bridging Table, as an alternative to learning them from incoming frames. These userdefined entries are not subject to aging, and are preserved across resets and reboots. TACACS+ provides centralized security for validation of users accessing the device. TACACS+ provides a centralized user management system, while still retaining consistency with RADIUS and other authentication processes. Transport Control Protocol (TCP). TCP connections are defined between 2 ports by an initial synchronization exchange. TCP ports are identified by an IP address and a 16-bit port number. Octets streams are divided into TCP packets, each carrying a sequence number. The device supports boot image, software and configuration upload/download via TFTP. Traceroute discovers IP routes that packets were forwarded along during the forwarding process. The CLI Traceroute utility can be executed from either the user-exec or privileged modes. VCT detects and reports copper link cabling occurrences, such as open cables and cable shorts. Page 330