HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches IRF Configuration Guide-R2 - Page 21
Accessing the IRF fabric, Accessing the CLI of the master switch
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 21 highlights
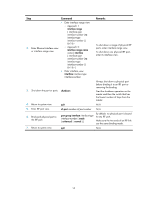
Step 8. Enter Ethernet interface view or interface range view. Command • Enter interface range view: { Approach 1: interface range { interface-type interface-number [ to interface-type interface-number ] } & { Approach 2: interface range name name [ interface { interface-type interface-number [ to interface-type interface-number ] } & ] • Enter interface view: interface interface-type interface-number 9. Bring up the port or ports. undo shutdown 10. Return to system view. quit 11. Save the running configuration. save 12. Activate the IRF port configuration. irf-port-configuration active Remarks N/A N/A N/A N/A After this step is performed, the state of the IRF port changes to UP, the member switches automatically elect a master, and the subordinate switch automatically reboots. After the IRF fabric is formed, you can add more physical ports to an IRF port (in UP state) without performing this step. Accessing the IRF fabric The IRF fabric appears as one device after it is formed. You configure and manage all IRF members at the CLI of the master. All settings you have made are automatically propagated to the IRF members. When you log in to an IRF fabric, you are placed at the CLI of the master, regardless of at which member switch you are logged in. After that, you can access the CLI of a subordinate switch to execute a limited set of maintenance commands. The IRF fabric supports up to 8 concurrent VTY users. The maximum number of concurrent console users equals the total number of member switches in the IRF fabric. Accessing the CLI of the master switch Access an IRF fabric in one of the following ways: • Local login-Log in through the console port of any member switch. 17