HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches IRF Configuration Guide-R2 - Page 26
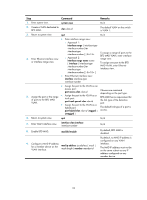
Configuring LACP MAD, mechanism, Advantages, Application scenario, Command, Remarks
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 26 highlights
Table 1 A comparison of the MAD mechanisms MAD mechanism LACP MAD BFD MAD ARP MAD Advantages Disadvantages Application scenario • Detection speed is fast. • Requires no MAD-dedicated physical ports or interfaces. Requires an intermediate HP device that supports LACP MAD packets. Link aggregation is used between the IRF fabric and its upstream or downstream device. For information about LACP, see Layer 2-LAN Switching Configuration Guide. • Suitable for various • Requires MAD dedicated network scenarios. physical ports and Layer • If no intermediate 3 interfaces, which device is used, this • Detection speed is fast. cannot be used for transmitting user traffic. mechanism is only suitable for IRF fabrics • No intermediate device is required. • If no intermediate device is used, the IRF members • Intermediate device, if used, must be fully meshed. can come from any vendor. • If an intermediate device that have a small number of members that are geographically close to one another. is used, every IRF member must connect to the intermediate device. For information about BFD, see High Availability Configuration Guide. • • No intermediate device is required. Intermediate device, if used, can come from any vendor. • Detection speed is slower than BFD MAD and LACP MAD. Spanning tree-enabled non-link aggregation IPv4 network scenario. For information about • Requires no MAD dedicated • Spanning tree feature ports. must be enabled. ARP, see Layer 3-IP Services Configuration Guide. Configuring LACP MAD When you use LACP MAD, follow these guidelines: • The intermediate device must be an HP device that support extended LACP for MAD. • If the intermediate device is in an IRF fabric, assign this fabric a different domain ID than the LACP MAD-enabled fabric to avoid false detection of IRF split. • Use dynamic link aggregation mode. MAD is LACP dependent. Even though LACP MAD can be configured on both static and dynamic aggregate interfaces, it takes effect only on dynamic aggregate interfaces. • Configure link aggregation settings also on the intermediate device. To configure LACP MAD: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 22