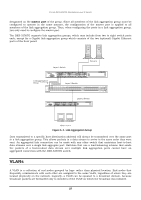
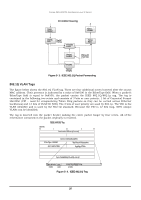
D-Link 3250TG Product Manual - Page 31
IP Addresses
 |
UPC - 790069250682
View all D-Link 3250TG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 31 highlights
D-Link DES-3250TG Standalone Layer 2 Switch IP Addresses The Internet Protocol (IP) was designed for routing data between network sites. Later, it was adapted for routing between networks (referred to as "subnets") within a site. The IP defines a way of generating a unique number that can be assigned each network in the Internet and each of the computers on each of those networks. This number is called the IP address. IP addresses use a "dotted decimal" notation. Here are some examples of IP addresses written in this format: 1. 210.202.204.205 2. 189.21.241.56 3. 125.87.0.1 This allows IP address to be written in a string of four decimal (base 10) numbers. Computers can only understand binary (base 2) numbers, and these binary numbers are usually grouped together in bytes, or eight bits. (A bit is a binary digit - either a "1" or a "0"). The dots (periods) simply make the IP address easier to read. A computer sees an IP address not as four decimal numbers, but as a long string of binary digits (32 binary digits or 32 bits, IP addresses are 32-bit addresses). The three IP addresses in the example above, written in binary form are: 1. 11010010.11001010.11001100.11001101 2. 10111101.00010101.11110001.00111000 3. 01111101.01010111.00000000.00000001 The dots are included to make the numbers easier to read. Eight binary bits are called a 'byte' or an 'octet'. An octet can represent any decimal value between '0' (00000000) and '255' (11111111). IP addresses, represented in decimal form, are four numbers whose value is between '0' to '255'. The total range of IP addresses are then: Lowest possible IP address Highest possible IP address - 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 To convert decimal numbers to 8-bit binary numbers (and vice-versa), you can use the following chart: Binary Octet Digit 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 2 0 Decimal Equivalent Binary Number 128+64+32+16+8+4+2+1= 255 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 11 Table 5- 2. Binary to Decimal Conversion Each digit in an 8-bit binary number (an octet) represents a power of two. The left-most digit represents 2 raised to the 7th power (2x2x2x2x2x2x2=128) while the right-most digit represents 2 raised to the 0th power (any number raised to the 0th power is equal to one, by definition). IP addresses actually consist of two parts, one identifying the network and one identifying the destination (node) within the network. The IP address discussed above is one part and a second number called the Subnet mask is the other part. To make this a bit more confusing, the subnet mask has the same numerical form as an IP address. 23