HP 3600dn HP Jetdirect Print Server Administrator's Guide - Page 35
Using the arp and ping Commands
 |
UPC - 829160888897
View all HP 3600dn manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 35 highlights
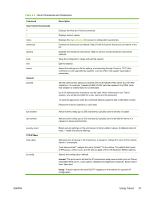
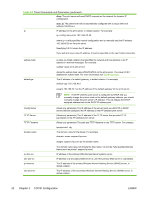
ping where is the assigned address from RARP. 10 If ping does not respond, see Troubleshooting the HP Jetdirect Print Server. Using the arp and ping Commands You can configure an HP Jetdirect print server with an IP address using an ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) command from a supported system. The protocol is not routable, that is, the workstation from which the configuration is made must be located on the same network segment as the HP Jetdirect print server. Using the arp and ping commands with HP Jetdirect print servers requires the following: ■ Windows NT/2000/XP/Server 2003 or UNIX system configured for TCP/IP operation ■ A legacy default IP address 192.0.0.192 has been set on the print server ■ The LAN hardware (MAC) address of the HP Jetdirect print server (specified on an HP Jetdirect configuration page) NOTE On some systems, superuser rights may be required for the arp command. After an IP address is assigned through arp and ping commands, use other tools (such as Telnet, embedded Web server, or HP Web Jetadmin software) to configure other IP parameters. To configure a Jetdirect print server, use the following commands: arp -s ping where is the desired IP address to be assigned to the print server. The arp command writes the entries to the arp cache on the workstation, and the ping command configures the IP address on the print server. Depending on the system, the LAN hardware address may require a specific format. For example: ■ For Windows NT 4.0, 2000, XP, Server 2003 arp -s 192.168.45.39 00-01-E6-a2-31-98 ping 192.168.45.39 ■ For UNIX arp -s 192.168.45.39 00:01:E6:a2:31:98 ping 192.168.45.39 ENWW Using the arp and ping Commands 27