HP Jetdirect 280m HP Jetdirect 280m 802.11b Wireless Internal Print Server LIO - Page 17
Wireless LANs
 |
View all HP Jetdirect 280m manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
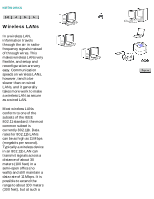
Network Basics NETWORKS Wireless LANs In a wireless LAN, information travels through the air in radiofrequency signals instead of through wires. This makes wireless LANs very flexible, and setup and reconfiguration are very easy. Communication speeds on wireless LANs, however, tend to be slower than on wired LANs, and it generally takes more work to make a wireless LAN as secure as a wired LAN. Most wireless LANs conform to one of the subsets of the IEEE 802.11 standard; the most common subset is currently 802.11b. Data rates for 802.11b LANs can be as high as 11 Mbps (megabits per second). Typically a wireless device in an 802.11b LAN can transmit signals across a distance of about 30 meters (100 feet) in a semi-open office (no walls) and still maintain a data rate of 11 Mbps. It is possible to extend the range to about 100 meters (300 feet), but at such a file:///C|/Bottlecap_Structure_26--TestMerge/DOCS/EN/NETBASIC/FNW0034.HTM (1 of 2) [5/20/2003 3:40:22 PM]