HP Jetdirect 280m HP Jetdirect 280m 802.11b Wireless Internal Print Server LIO - Page 30
Addresses, Internet Protocol IP.
 |
View all HP Jetdirect 280m manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
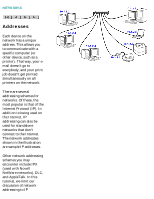
Network Basics NETWORKS Addresses Each device on the network has a unique address. This allows you to communicate with a specific computer (or other device, such as a printer). That way, your email doesn't go to everybody, and your print job doesn't get printed simultaneously on all printers on the network. There are several addressing schemes for networks. Of these, the most popular is that of the Internet Protocol (IP). In addition to being used on the Internet, IP addressing can also be used for standalone networks that don't connect to the Internet. The network addresses shown in the illustration are sample IP addresses. Other network addressing schemes you may encounter include IPX (used with Novell NetWare networks), DLC, and AppleTalk. In this tutorial, we limit our discussion of network addressing to IP file:///C|/Bottlecap_Structure_26--TestMerge/DOCS/EN/NETBASIC/FNW0050.HTM (1 of 2) [5/20/2003 3:44:31 PM]