HP c3700 hp Visualize b2000 UNIX workstation service handbook (a5983-90039) - Page 79
Running ODE-Based Diagnostics, Using the PIM Dump Tool to Decode HPMCs
 |
View all HP c3700 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 79 highlights
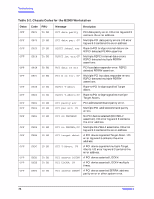
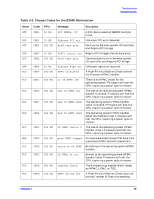
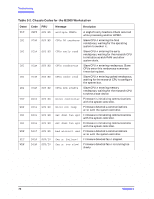
Troubleshooting Running ODE-Based Diagnostics Running ODE-Based Diagnostics The Offline Diagnostic Environment (ODE) consists of diagnostic modules for testing and verifying system operation. ODE provides all the necessary functions for the user to load specified tests and interact with those tests. ODE is an ISL utility. To boot ODE: 1. Invoke the ISL environment from the system disk or CD. 2. Type ode Enter after the ISL> prompt to invoke ODE from the LIF directory on the system disk. The prompt changes to ODE>. Not all of the test modules are available on all systems. To see what test modules are available to run on this system, type ls at the ODE> prompt. The available modules include the following: • wdiag - tests and verifies the basic functionality of the PA-RISC chip. This tool tests the CPU, cache, TLB, and floating point functions. • memtest - tests and verifies the memory arrays. If an error is detected, the diagnostic reports the memory card and its slot number that needs replacement. It also provides a map of the memory configuration so that the user can identify the types of memory and its slot location. • mapper - identifies the configuration of HPPA systems. It displays path, identification, and revision information of I/O components, configuration of memory controllers, processors, co-processors, cache, and TLB, as well as processor board component revisions and values of various HPPA system identifiers, revisions, and capabilities. • astrodiag - tests and verifies the basic functionality of the Astro memory/IO controller chip. • siodiag - tests and verifies the functionality of the super IO multifunction IO chip, including serial, parallel, USB, and so forth. For further information on the various ODE commands and a complete listing of the command set, type help Enter at the ODE> prompt or at the prompt of one of the test modules. Using the PIM Dump Tool to Decode HPMCs If the system HPMC and halts, the Boot Console Handler's Service menu provides a PIM dump tool that can analyze the HPMC dump and attempt to decode it for analysis. It will point to the failing FRU or memory location if it is memory related. For information on using the Boot Console Handler, see Chapter 6. Chapter 3 79