HP d640 HP D640 High-Volume Printer - Technical Reference Manual, C5630-90030 - Page 15
Left Offset, Top Offset, Orientation, Reserved Byte, Width, Table 2, Logical Format
 |
View all HP d640 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
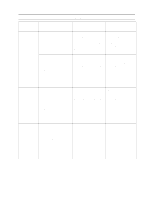
If you define text to start printing at location 0,0 it will print off of the logical page. This may or may not be on the physical page. Figure 1 describes the physical and logical page formats. The following escape sequence allows you to define the logical page: & a # W[binary data] Where # is the number of bytes of binary data following the terminator. The default value for # is = NA. The range for # is = 4,10. The binary data describes the logical page format as shown below: Table 2 Logical Page Format Byte 0 2 4 6 8 15 (MSB) Orientation 8 7 0 (LSB) Left Offset Top Offset Reserved (0) Width Height Byte 1 3 5 7 9 Left Offset Specifies (in integer decipoints) the location of the left edge of the logical page with respect to the left side of the physical page in the selected viewing orientation. The range of values is -32767 to 32767. Top Offset Specifies (in integer decipoints) the location of the top edge of the logical page with respect to the top edge of the physical page in the selected viewing orientation. The range of values is -32767 to 32767. Orientation This is the viewing orientation of the logical page with respect to the physical page. Values may be 0 (portrait), 1 (landscape), 2 (reverse portrait), or 3 (reverse landscape). All other values reset the logical page definition leaving the logical page as it was previously defined. Reserved Byte A byte which must be present in the data stream and must be equal to zero. Width Logical page width is defined in decipoints. A zero width causes the logical page definition to be ignored. The logical page may be larger than the physical page. The range of values is 1 to 65535. Chapter 2: Printing Options 9